Identification and characterization of a core fucosidase from the bacterium Elizabethkingia meningoseptica
- PMID: 29196602
- PMCID: PMC5787802
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.804252
Identification and characterization of a core fucosidase from the bacterium Elizabethkingia meningoseptica
Abstract
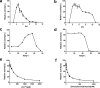
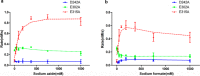
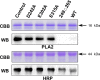
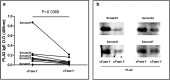
All reported α-l-fucosidases catalyze the removal of nonreducing terminal l-fucoses from oligosaccharides or their conjugates, while having no capacity to hydrolyze core fucoses in glycoproteins directly. Here, we identified an α-fucosidase from the bacterium Elizabethkingia meningoseptica with catalytic activity against core α-1,3-fucosylated substrates, and we named it core fucosidase I (cFase I). Using site-specific mutational analysis, we found that three acidic residues (Asp-242, Glu-302, and Glu-315) in the predicted active pocket are critical for cFase I activity, with Asp-242 and Glu-315 acting as a pair of classic nucleophile and acid/base residues and Glu-302 acting in an as yet undefined role. These findings suggest a catalytic mechanism for cFase I that is different from known α-fucosidase catalytic models. In summary, cFase I exhibits glycosidase activity that removes core α-1,3-fucoses from substrates, suggesting cFase I as a new tool for glycobiology, especially for studies of proteins with core fucosylation.
Keywords: allergy; chemical rescue; core fucosidase; core α-1,3 fucosylation; core α-1,3-fucose; glycobiology; glycoprotein; mass spectrometry (MS); mutagenesis; oligosaccharide.
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

