A Brief Instrument to Assess Both Burnout and Professional Fulfillment in Physicians: Reliability and Validity, Including Correlation with Self-Reported Medical Errors, in a Sample of Resident and Practicing Physicians
- PMID: 29196982
- PMCID: PMC5794850
- DOI: 10.1007/s40596-017-0849-3
A Brief Instrument to Assess Both Burnout and Professional Fulfillment in Physicians: Reliability and Validity, Including Correlation with Self-Reported Medical Errors, in a Sample of Resident and Practicing Physicians
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the performance of the Professional Fulfillment Index (PFI), a 16-item instrument to assess physicians' professional fulfillment and burnout, designed for sensitivity to change attributable to interventions or other factors affecting physician well-being.
Methods: A sample of 250 physicians completed the PFI, a measure of self-reported medical errors, and previously validated measures including the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI), a one-item burnout measure, the World Health Organization's abbreviated quality of life assessment (WHOQOL-BREF), and PROMIS short-form depression, anxiety, and sleep-related impairment scales. Between 2 and 3 weeks later, 227 (91%) repeated the PFI and the sleep-related impairment scale.
Results: Principal components analysis justified PFI subscales for professional fulfillment, work exhaustion, and interpersonal disengagement. Test-retest reliability estimates were 0.82 for professional fulfillment (α = 0.91), 0.80 for work exhaustion (α = 0.86), 0.71 for interpersonal disengagement (α = 0.92), and 0.80 for overall burnout (α = 0.92). PFI burnout measures correlated highly (r ≥ 0.50) with their closest related MBI equivalents. Cohen's d effect size differences in self-reported medical errors for high versus low burnout classified using the PFI and the MBI were 0.55 and 0.44, respectively. PFI scales correlated in expected directions with sleep-related impairment, depression, anxiety, and WHOQOL-BREF scores. PFI scales demonstrated sufficient sensitivity to detect expected effects of a two-point (range 8-40) change in sleep-related impairment.
Conclusions: PFI scales have good performance characteristics including sensitivity to change and offer a novel contribution by assessing professional fulfillment in addition to burnout.
Figures
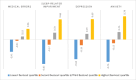
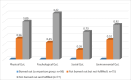
References
-
- Wallace JE, Lemaire JB, Ghali WA. Physician wellness: a missing quality indicator. Lancet. 2009;374(9702):1714–21. - PubMed
-
- Shanafelt TD, Sloan JA, Habermann TM. The well-being of physicians. Am J Med. 2003;114(6):513–9. - PubMed
-
- Shanafelt TD, Boone S, Tan L, Dyrbye LN, Sotile W, Satele D, et al. Burnout and satisfaction with work-life balance among US physicians relative to the general US population. Arch Intern Med. 2012;172(18):1377–85. - PubMed
-
- Shanafelt TD, Hasan O, Dyrbye LN, Sinsky C, Satele D, Sloan J, et al. Changes in burnout and satisfaction with work-life balance in physicians and the general US working population between 2011 and 2014. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90(12):1600–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

