Trends in prevalence, mortality, health care utilization and health care costs of Swiss IBD patients: a claims data based study of the years 2010, 2012 and 2014
- PMID: 29197335
- PMCID: PMC5712179
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-017-0681-y
Trends in prevalence, mortality, health care utilization and health care costs of Swiss IBD patients: a claims data based study of the years 2010, 2012 and 2014
Abstract
Background: Real-life data on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) prevalence and costs are scarce. The aims of this study were to provide an overview of the prevalence, mortality, health care utilization and costs of IBD patients in Switzerland in the years 2010, 2012, and 2014.
Methods: Based on claims data of the Helsana-Group, prevalence of IBD was assessed for 2010, 2012 and 2014. Mortality rates, costs (inpatient, outpatient, medication costs) and utilization (visits, hospitalizations) were compared between patients with and without IBD, and between IBD patients treated with and without biologics. Results were extrapolated to the Swiss general population using national census data. Multivariate linear regression was used to identify socio-demographic and regional factors influencing total costs.
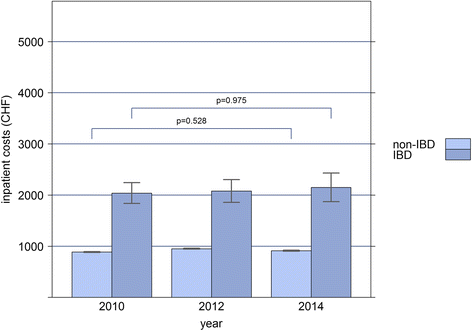
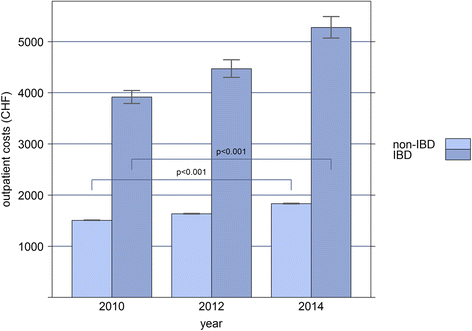
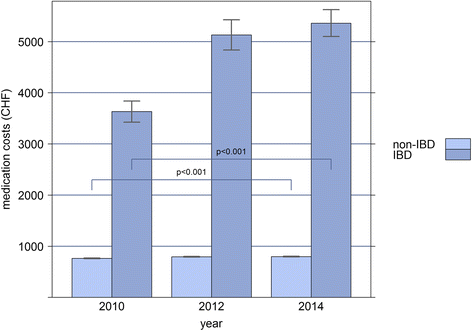
Results: The overall extrapolated prevalence rates of IBD were 0.32% in 2010, 0.38% in 2012, and 0.41% in 2014. Mortality rate didn't differ between the IBD and non-IBD population. Costs increased annually by 6% in IBD versus 2.4% in non-IBD subjects, which was solely due to increased outpatient costs. Almost one-fourth of IBD patients were hospitalized at least once a year. Costs were higher in IBD patients treated with biologics (OR = 3.98, CI: 3.72-4.27, p < 0.001) when compared to IBD patients without biologic therapies. Over 70% of the total costs in IBD patients treated with biologics were due to drug costs, compared with 28% in patients without use of biologic therapies, whereas inpatient costs didn't differ.
Conclusions: The prevalence of IBD seems to be increasing in Switzerland. Outpatient costs increased substantially, while no decrease in inpatient costs was found. Treatment of IBD is more and more based on biologic therapies.
Keywords: Health care costs; Inflammatory bowel disease; Mortality; Prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
According to the Swiss Federal Law on data protection, this study was exempted from ethics committee approval as all data were anonymized, retrospective, pre-existing, and de-identified in order to protect the privacy of patients, physicians, and hospitals. The study protocol was approved by the Helsana Group.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
SRV consulted and received speaker’s honoraria from Abbvie, UCB, Falk, MSD, Tillots, Vifor, Pfizer, Takeda, and Ferring. AS consulted and received speaker’s honoraria from Abbvie, UCB, Falk, MSD, Tillotts, Vifor, Pfizer, Takeda, Ferring, Receptos, and Takeda.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

