Evaluation of the new TNM-staging system for thymic malignancies: impact on indication and survival
- PMID: 29197400
- PMCID: PMC5712125
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-017-1283-4
Evaluation of the new TNM-staging system for thymic malignancies: impact on indication and survival
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study is the evaluation of the Masaoka-Koga and the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC)/International Thymic Malignancy Interest Group (ITMIG) proposal for the new TNM-staging system on clinical implementation and prognosis of thymic malignancies.
Methods: A retrospective study of 76 patients who underwent surgery between January 2005 and December 2015 for thymoma. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to determine overall and recurrence-free survival rates.
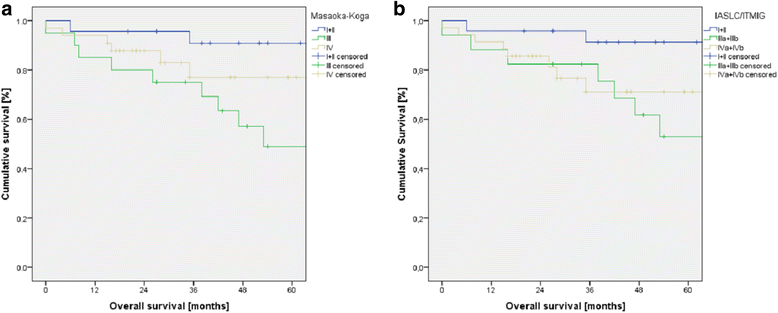
Results: Indication for surgery was primary mediastinal tumor (n = 55), pleural manifestation (n = 17), or mediastinal recurrence (n = 4) after surgery for thymoma. Early Masaoka-Koga stages I (n = 9) and II (n = 14) shifted to the new stage I (n = 23). Advanced stages III (Masaoka-Koga: n = 20; ITMIG/IASLC: n = 17) and IV (Masaoka-Koga: n = 33; ITMIG/IASLC: n = 35) remained nearly similar and were associated with higher levels of WHO stages. Within each staging system, the survival curves differed significantly with the best 5-year survival in early stages I and II (91%). Survival for stage IV (70 to 77%) was significantly better compared to stage III (49 to 54%). Early stages had a significant longer recurrence-free survival (86 to 90%) than advanced stages III and IV (55 to 56%).
Conclusions: The proportion of patients with IASLC/ITMIG stage I increased remarkably, whereas the distribution in advanced stages III and IV was nearly similar. The new TNM-staging system presents a clinically useful and applicable system, which can be used for indication, stage-adapted therapy, and prediction of prognosis for overall and recurrence-free survival.
Keywords: Masaoka-Koga; Staging system; TNM staging; Thymic carcinoma; Thymoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by our Institutional Review Board (University Hospital Regensburg), which waived the requirement for an individual patient consent because only routine patient data were used for this retrospective analysis.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

