Challenging and uncommon diagnosis of long-evolution ascites
- PMID: 29197848
- PMCID: PMC5720252
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-222565
Challenging and uncommon diagnosis of long-evolution ascites
Abstract
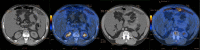
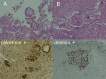
This is a case report of a 45-year-old Caucasian man with chronic alcoholism. No history of liver disease or asbestos exposure. He complained of ascites during the last 3 years with worsening in the last year with severe ascites development. Diagnostic paracentesis showed SAAG 1.1 and high cellularity with neutrophil count >250 cells/µL. Ascitic fluid cytology revealed reactive mesothelial hyperplasia. Thoracoabdominopelvic ultrasonography/CT/MRI and fludeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/CT showed 'omental cake' pattern suggesting peritoneal carcinomatosis. An exploratory laparoscopy revealed moderate interloop adhesions and necrosis with whitish exudate in the right pelvic excavation. Biochemical/cytological/histological/microbiological study only revealed reactive mesothelial cells, necrosis and lymphohistiocytic inflammatory infiltrate. A second exploratory laparoscopy with liver and peritoneal biopsies and appendectomy/mesoappendix excision showed a well-differentiated tubulopapillary mesothelioma. The patient was referred for intraperitoneal chemotherapy and is undergoing monthly therapeutic paracentesis.
Keywords: gastroenterology; gastrointestinal surgery; gastrointestinal system; malignant disease and immunosuppression.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Kumar BA, Gogineni S, Suneetha C, et al. . A rare case of well differentiated papillary mesothelioma of peritoneal origin. J Dent Med Sci 2013;6:01–4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
