Identification of Key Genes in Colorectal Cancer Regulated by miR-34a
- PMID: 29197895
- PMCID: PMC5724350
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.904937
Identification of Key Genes in Colorectal Cancer Regulated by miR-34a
Abstract
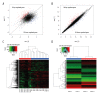
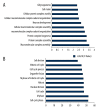
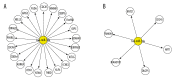
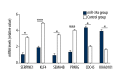
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to screen the molecular targets of miR-34a in colorectal cancer (CRC) and construct the regulatory network, to gain more insights to the pathogenesis of CRC. MATERIAL AND METHODS The microarray data of CRC samples and normal samples (GSE4988), as well as CRC samples transformed with miR-34a and non-transfected CRC samples (GSE7754), were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The differently expressed genes (DEGs) were identified via the LIMMA package in R language. The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) was used to identify significant Gene Ontology (GO) terms and pathways in DEGs. The targets of miR-34a were obtained via the miRWalk database, and then the overlaps between them were selected out to construct the regulatory network of miR-34a in CRC using the Cytoscape software. RESULTS A total of 392 DEGs were identified in CRC samples compared with normal samples, including 239 upregulated genes and 153 downregulated ones. These DEGs were enriched in 75 GO terms and one Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway. At the same time, 332 DEGs (188 upregulated and 144 downregulated) were screened out between miR-34a transformed CRC and miR-34a non-transfected CRC samples and they were enriched in 20 GO terms and eight KEGG pathways. Six overlapped genes were identified in two DEGs groups. There were 1,668 targets of miR-34a obtained via the miRWalk database, among which 21 were identified differently expressed in miR-34a transformed CRC samples compared with miR-34a non-transfected CRC samples. Two regulatory networks of miR-34a in CRC within these two groups of overlapped genes were constructed respectively. CONCLUSIONS Pathways related to cell cycle, DNA replication, oocyte meiosis, and pyrimidine metabolism might play critical roles in the progression of CRC. Several genes such as SERPINE1, KLF4, SEMA4B, PPARG, CDC45, and KIAA0101 might be the targets of miR-34a and the potential therapeutic targets of CRC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics, 2000. Cancer J Clin. 2000;50:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Pasetto LM, Monfardini S. Colorectal cancer screening in elderly patients: When should be more useful? Cancer Treat Rev. 2007;33:528–32. - PubMed
-
- Obrand DI, Gordon PH. Incidence and patterns of recurrence following curative resection for colorectal carcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum. 1997;40:15–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

