The coronavirus nucleocapsid protein is ADP-ribosylated
- PMID: 29199039
- PMCID: PMC5871557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.11.020
The coronavirus nucleocapsid protein is ADP-ribosylated
Abstract
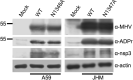
ADP-ribosylation is a common post-translational modification, although how it modulates RNA virus infection is not well understood. While screening for ADP-ribosylated proteins during coronavirus (CoV) infection, we detected a ~55kDa ADP-ribosylated protein in mouse hepatitis virus (MHV)-infected cells and in virions, which we identified as the viral nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N proteins of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-CoV were also ADP-ribosylated. ADP-ribosylation of N protein was also observed in cells exogenously expressing N protein by transduction using Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus replicon particles (VRPs). However, plasmid-derived N protein was not ADP-ribosylated following transient transfection but was ADP-ribosylated after MHV infection, indicating that this modification requires virus infection. In conclusion, we have identified a novel post-translation modification of the CoV N protein that may play a regulatory role for this important structural protein.
Keywords: ADP-ribosylation; Coronavirus; MERS-CoV; Macrodomain; Mouse hepatitis virus; Nucleocapsid; PEDV; SARS-CoV.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Bernardi R., Rossi L., Poirier G.G., Scovassi A.I. Analysis of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase activity in nuclear extracts from mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1997;1338:60–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

