Long-term renal and overall survival of critically ill patients with acute renal injury who received continuous renal replacement therapy
- PMID: 29199512
- PMCID: PMC6446161
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1398667
Long-term renal and overall survival of critically ill patients with acute renal injury who received continuous renal replacement therapy
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with the increased short-term mortality of critically ill patients on continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). The aim of this research was to evaluate the association of kidney function at discharge with the long-term renal and overall survival of critically ill patients with AKI who were on CRRT in an intensive care unit (ICU).
Methods: We retrospectively collected data for critically ill patients with AKI who were admitted to ICU on CRRT at a tertiary metropolitan hospital in China between 2008 and 2013. The patients were followed up to their death or to 30 September 2016 by telephone.
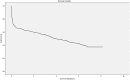
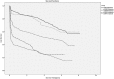
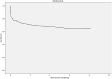
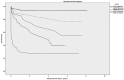
Results: A total of 403 patients were enrolled in this study. The 1-, 3- and 5-year patient survival rates were 64.3 ± 2.4, 55.8 ± 2.5 and 46.3 ± 2.7%, respectively. In multivariate analysis, age, sepsis, decreased renal perfusion (including volume contraction, congestive heart failure, hypotension and cardiac arrest), preexisting kidney disease, Apache II score, Saps II score, vasopressors and eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 at discharge were independent factors for worse long-term patient survival. And age, preexisting kidney disease, Apache II score, mechanical ventilation (MV) and eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 at discharge were also associated with worse renal survival.
Conclusions: This study showed that impaired kidney function at discharge was shown to be an important risk factor affecting the long-term renal survival rates of critically ill patients with AKI. An eGFR <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 was an independent risk factor for decreased overall survival and renal survival.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; continuous renal replacement therapy; critically ill; long-term survival.
Figures
References
-
- Bagshaw SM, George C, Bellomo R, et al. A comparison of the RIFLE and AKIN criteria for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:1569–1574. - PubMed
-
- Ftough S, Lewington A. Guideline development group convened by the National Clinical Guidelines Centre and commissioned by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in association with The Royal College of Physicians’ Clinical Effectiveness and Evaluation Unit . Prevention, detection and management of acute kidney injury. Clin Med. 2014;14:61–65.
-
- Kidney Disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Inter Suppl. 2012;2:1–138.
-
- Fang Y, Ding X, Zhong Y, et al. Acute kidney injury in a Chinese hospitalized population. Blood Purif. 2010;30:120–126. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
