Peritoneal dialysis for acute kidney injury
- PMID: 29199769
- PMCID: PMC6486317
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011457.pub2
Peritoneal dialysis for acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Peritoneal dialysis (PD) has been suggested as an effective and safe dialysis modality in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). However, whether PD is superior to extracorporeal therapy (e.g. haemodialysis) in terms of improving survival, recovery of kidney function, metabolic and clinical outcomes is still inconclusive.
Objectives: The aim of this review was to evaluate the benefits and harms of PD for patients with AKI compared with extracorporeal therapy or different PD modalities.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Kidney and Transplant Register of Studies to 29 May 2017 through contact with the Information Specialist using search terms relevant to this review. Studies in the Register are identified through searches of CENTRAL, MEDLINE, and EMBASE, conference proceedings, the International Clinical Trials Register (ICTRP) Search Portal, and ClinicalTrials.gov. We also searched the China Biological Medicine Database.
Selection criteria: We included patients with AKI who were randomised to receive PD, extracorporeal therapy, or different PD modalities regardless of their age, sex, primary disease and clinical course.
Data collection and analysis: Screening, selection, data extraction and quality assessments for each retrieved article were carried out by two authors using standardised forms. Authors contacted when published data were incomplete. Statistical analyses were performed using the random effects model and results expressed as risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity among studies was explored using the Cochran Q statistic and the I2 test. Outcomes of interest included all-cause mortality, recovery of kidney function, weekly delivered Kt/V, correction of acidosis, fluid removal, duration of dialysis, and infectious complications. Confidence in the evidence was assessing using GRADE.
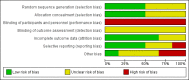
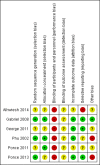
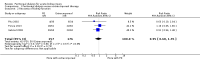
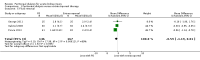
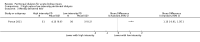
Main results: Six studies (484 participants) met our inclusion criteria. Five studies compared high volume PD with daily haemodialysis, extended daily haemodialysis, or continuous renal replacement therapy. One study focused on the intensity of PD. The overall risk of bias was low to unclear. Compared to extracorporeal therapy, PD probably made little or no difference to all-cause mortality (4 studies, 383 participants: RR 1.12, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.55; I2 = 69%; moderate certainty evidence), or kidney function recovery (3 studies, 333 participants: RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.35; I2 = 0%; moderate certainty evidence). PD probably slightly reduces the amount of fluid removal compared to extracorporeal therapy (3 studies, 313 participants: MD -0.59 L/d, 95% CI -1.19 to 0.01; I2 = 89%; low certainty evidence), and probably made little or no difference to infectious complications (2 studies, 263 participants: RR 1.03, 95% CI 0.60 to 1.78; I2 = 0%; low certainty evidence). It is uncertain whether PD compared to extracorporeal therapy has any effects on weekly delivered Kt/V (2 studies, 263 participants: MD -2.47, 95% CI -5.17 to 0.22; I2 = 99%; very low certainty evidence), correction of acidosis (2 studies, 89 participants: RR 1.32, 95% CI 0.13 to 13.60; I2 = 96%; very low certainty evidence), or duration of dialysis (2 studies, 170 participants: MD -1.01 hours, 95% CI -91.49 to 89.47; I2 = 98%; very low certainty evidence). Heterogeneity was high and this may be due to the different extracorporeal therapies used.One study (61 participants) reported little or no difference to all-cause mortality, kidney function recovery, or infection between low and high and intensity PD. Weekly delivered Kt/V and fluid removal was lower with low compared to high intensity PD.
Authors' conclusions: Based on moderate (mortality, recovery of kidney function), low (infectious complications), or very low certainty evidence (correction of acidosis) there is probably little or no difference between PD and extracorporeal therapy for treating AKI. Fluid removal (low certainty) and weekly delivered Kt/V (very low certainty) may be higher with extracorporeal therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Linfeng Liu: none known
Ling Zhang: none known
Guan J Liu: none known
Ping Fu: none known.
Figures









Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Alhwiesh 2014 {published data only}
-
- Alhwiesh A, Nasreldin MA, Saeed I. Comparing tidal peritoneal dialysis to CRRT in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. A single centre experience [abstract no: SP461]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2014;29(Suppl 3):iii226. [EMBASE: 71492088]
Gabriel 2008 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Gabriel DP, Caramori JT, Martim LC, Barretti P, Balbi AL. High volume peritoneal dialysis vs daily hemodialysis: a randomized, controlled trial in patients with acute kidney injury. Kidney International ‐ Supplement 2008, (108):S87‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gabriel DP, Caramori JT, Martin LC, Barretti P, Balbi AL. Continuous peritoneal dialysis compared with daily hemodialysis in patients with acute kidney injury. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2009;29 Suppl 2:S62‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
George 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- George J, Pisharody R, Upendran B, Varma S, Leelakumari M, Palliyil S. Clinical trial of continuous veno venous hemodiafiltration and peritoneal dialysis in critically ill acute renal failure [abstract no: SaP218]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2007;22(Suppl 6):vi305.
-
- George J, Varma S, Kumar S, Thomas J, Gopi S, Pisharody R. Comparing continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration and peritoneal dialysis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury: a pilot study. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2011;31(4):422‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Phu 2002 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Bazari H. Hemofiltration and peritoneal dialysis in infection‐associated acute renal failure. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348(9):858‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Casserly LF. Hemofiltration and peritoneal dialysis in infection‐associated acute renal failure. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348(9):858‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Daugirdas JT. Peritoneal dialysis in acute renal failure‐‐why the bad outcome?. New England Journal of Medicine 2002; Vol. 347, issue 12:933‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Fruchter O. Hemofiltration and peritoneal dialysis in infection‐associated acute renal failure. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348(9):858‐60. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Phu NH, Hien TT, Mai NT, Chau TT, Chuong LV, Loc PP, et al. Hemofiltration and peritoneal dialysis in infection‐associated acute renal failure in Vietnam. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;347(12):895‐902. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ponce 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ponce D, Balbi AL. Different prescribed doses of high volume peritoneal dialysis and outcome of patients with acute kidney injury [abstract]. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2012;32(Suppl 3):S4. [EMBASE: 71927756] - PubMed
-
- Ponce D, Brito GA, Abrao JG, Balb AL. Different prescribed doses of high‐volume peritoneal dialysis and outcome of patients with acute kidney injury. Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis 2011;27(1):118‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ponce 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ponce D, Balbi AL, Abrao JM, Berbel MN, Pinto MP, Brito GA. High volume peritoneal dialysis (PD) versus sustained low efficiency dialysis: a randomized controlled trial in patients with acute kidney injury: initial results [abstract]. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2012;32:S4. [EMBASE: 71927757]
-
- Ponce D, Berbel MN, Abrao JM, Goes CR, Balbi AL. A randomized clinical trial of high volume peritoneal dialysis versus extended daily hemodialysis for acute kidney injury patients. International Urology & Nephrology 2013;45(3):869‐78. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Arogundade 2005 {published data only}
-
- Arogundade FA, Ishola DA Jr, Sanusi AA, Akinsola A. An analysis of the effectiveness and benefits of peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis using Nigerian made PD fluids. African Journal of Medicine & Medical Sciences 2005;34(3):227‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chitalia 2002 {published data only}
-
- Chitalia VC, Almeida AF, Rai H, Bapat M, Chitalia KV, Acharya VN, et al. Is peritoneal dialysis adequate for hypercatabolic acute renal failure in developing countries?. Kidney International 2002;61(2):747‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chitalia VC, Fernandes A, Rai H, Bapat M, Chitalia KV, Acharya VN, et al. Is peritoneal dialysis adequate for hypercatabolic acute renal failure? [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):447A. [CENTRAL: CN‐00550689]
Kalra 1989 {published data only}
-
- Kalra OP, Abrol L, Chopra JS, Agarwal SK, Prakash C. Optimal exchange volume and dialysate flow rate in peritoneal dialysis. A clinical study. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 1989;37(12):762‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nand 1996 {published data only}
-
- Nand N, Mahajan SK, Wig N, Sharma M, Aggarwal HK, Seth RK. Comparison of sodium nitroprusside added peritoneal dialysis and standard haemodialysis. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 1996;44(11):780‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nand 1997a {published data only}
-
- Nand N, Agarwal HK, Mahajan SK, Thukral S, Sharma M, Kumar P. Evaluation of efficacy of standard haemodialysis and verapamil added peritoneal dialysis. Indian Journal of Medical Sciences 1997;51(3):75‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Basu 2016
-
- Basu B, Mahapatra TK, Roy B, Schaefer F. Efficacy and outcomes of continuous peritoneal dialysis versus daily intermittent hemodialysis in pediatric acute kidney injury. Pediatric Nephrology 2016;31(10):1681‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bunchman 1994
-
- Bunchman TE, Donckerwolke RA. Continuous arterial‐venous diahemofiltration and continuous veno‐venous diahemofiltration in infants and children. Pediatric Nephrology 1994;8(1):96‐102. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cerda 2008
-
- Cerda J, Bagga A, Kher V, Chakravarthi RM. The contrasting characteristics of acute kidney injury in developed and developing countries. Nature Clinical Practice Nephrology 2008;4(3):138–53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chatterjee 2009
-
- Chatterjee S, Todi S, Sahu S, Bhattacharya M. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in India [abstract]. Critical Care 2009;13(Suppl 1):S141. [EMBASE: 70188340]
Chionh 2013
Cullis 2014
Dell'Aquila 2006
-
- Dell'Aquila R, Rodighiero MP, Spano E, Feriani M, Ronco C. Acid‐base balance in peritoneal dialysis. Journal of Nephrology 2006;19 Suppl 9:S104‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ellis 1997
-
- Ellis EN, Pearson D, Belsha CW, Berry PL. Use of pump‐assisted hemofiltration in children with acute renal failure. Pediatric Nephrology 1997;11(2):196‐200. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gabriel 2006
-
- Gabriel DP, Nascimento GV, Caramori JT, Martim LC, Barretti P, Balbi AL. Peritoneal dialysis in acute renal failure. Renal Failure 2006;28(6):451‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gabriel 2007a
-
- Gabriel DP, Nascimento GV, Caramori JT, Martim LC, Barretti P, Balbi AL. High volume peritoneal dialysis for acute renal failure. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2007;27(3):277‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gabriel 2007b
-
- Gabriel DP, Fernández‐Cean J, Balbi AL. Utilization of peritoneal dialysis in the acute setting. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2007;27(3):328‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GRADE 2008
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Himmelfarb 2007
-
- Himmelfarb J, Ikizler TA. Acute kidney injury: changing lexicography, definitions, and epidemiology. Kidney International 2007;71(10):971–6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hoste 2006
Hsu 2013
Hyman 2002
-
- Hyman A, Mendelssohn DC. Current Canadian approaches to dialysis for acute renal failure in the ICU. American Journal of Nephrology 2002;22(1):29‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jeloka 2006
-
- Jeloka TK, Ersoy FF, Yavuz M, Sahu KM, Camsari T, Utas C, et al. What is the optimal dwell time for maximizing ultrafiltration with icodextrin exchange in automated peritoneal dialysis patients?. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2006;26(3):336–40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mehta 2007
Mohandas 2004
-
- Mohandas N, Chellapandian D. Value of intermittent peritoneal dialysis in rural setup. Indian Journal of Peritoneal Dialysis 2004;6(1):19‐20.
Piccinni 2011
-
- Piccinni P, Cruz DN, Gramaticopolo S, Garzotto F, Dal Santo M, Aneloni G, et al. Prospective multicenter study on epidemiology of acute kidney injury in the ICU: a critical care nephrology Italian collaborative effort (NEFROINT). Minerva Anestesiologica 2011;77(11):1072‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ponce 2012
-
- Ponce D, Balbi AL, Amerling R. Advances in peritoneal dialysis in acute kidney injury. Blood Purification 2012;34(2):107‐16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ricci 2006
-
- Ricci Z, Ronco C, D’amico G, Felice R, Rossi S, Bolgan I, et al. Practice patterns in the management of acute renal failure in the critically ill patient: an international survey. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2006;21(3):690–6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ronco 2006
-
- Ronco C. Factors affecting hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis efficiency. Contributions to Nephrology 2006;150:1–12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schiffl 2002
-
- Schiffl H, Lang SM, Fischer R. Daily hemodialysis and the outcome of acute renal failure. New England Journal of Medicine 2002;346(5):305–10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Sharma 2003
-
- Sharma SK, Manandhar D, Singh J, Chauhan HS, Koirala B, Gautam M, et al. Acute peritoneal dialysis in Eastern Nepal. Peritoneal Dialysis International 2003;23 Suppl 2:S196‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Susantitaphong 2013
Uchino 2005
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. The Journal of the American Medical Association 2005;294(7):813–8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

