Characterization of dFOXO binding sites upstream of the Insulin Receptor P2 promoter across the Drosophila phylogeny
- PMID: 29200426
- PMCID: PMC5714339
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188357
Characterization of dFOXO binding sites upstream of the Insulin Receptor P2 promoter across the Drosophila phylogeny
Abstract
The insulin/TOR signal transduction pathway plays a critical role in determining such important traits as body and organ size, metabolic homeostasis and life span. Although this pathway is highly conserved across the animal kingdom, the affected traits can exhibit important differences even between closely related species. Evolutionary studies of regulatory regions require the reliable identification of transcription factor binding sites. Here we have focused on the Insulin Receptor (InR) expression from its P2 promoter in the Drosophila genus, which in D. melanogaster is up-regulated by hypophosphorylated Drosophila FOXO (dFOXO). We have finely characterized this transcription factor binding sites in vitro along the 1.3 kb region upstream of the InR P2 promoter in five Drosophila species. Moreover, we have tested the effect of mutations in the characterized dFOXO sites of D. melanogaster in transgenic flies. The number of experimentally established binding sites varies across the 1.3 kb region of any particular species, and their distribution also differs among species. In D. melanogaster, InR expression from P2 is differentially affected by dFOXO binding sites at the proximal and distal halves of the species 1.3 kb fragment. The observed uneven distribution of binding sites across this fragment might underlie their differential contribution to regulate InR transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
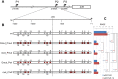
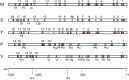
References
-
- Garofalo RS. Genetic analysis of insulin signaling in Drosophila. Trends Endocrinol Metab. Elsevier; 2002;13: 156–162. doi: 10.1016/S1043-2760(01)00548-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brogiolo W, Stocker H, Ikeya T, Rintelen F, Fernandez R, Hafen E. An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control. Curr Biol. 2001;11: 213–221. - PubMed
-
- Tatar M, Kopelman A, Epstein D, Tu MP, Yin CM, Garofalo RS. A mutant Drosophila insulin receptor homolog that extends life-span and impairs neuroendocrine function. Science. 2001;292: 107–110. doi: 10.1126/science.1057987 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kenyon CJ. The genetics of ageing. Nature. Nature Publishing Group; 2010;464: 504–512. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

