A model of individualized canonical microcircuits supporting cognitive operations
- PMID: 29200435
- PMCID: PMC5714354
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188003
A model of individualized canonical microcircuits supporting cognitive operations
Abstract
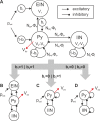
Major cognitive functions such as language, memory, and decision-making are thought to rely on distributed networks of a large number of basic elements, called canonical microcircuits. In this theoretical study we propose a novel canonical microcircuit model and find that it supports two basic computational operations: a gating mechanism and working memory. By means of bifurcation analysis we systematically investigate the dynamical behavior of the canonical microcircuit with respect to parameters that govern the local network balance, that is, the relationship between excitation and inhibition, and key intrinsic feedback architectures of canonical microcircuits. We relate the local behavior of the canonical microcircuit to cognitive processing and demonstrate how a network of interacting canonical microcircuits enables the establishment of spatiotemporal sequences in the context of syntax parsing during sentence comprehension. This study provides a framework for using individualized canonical microcircuits for the construction of biologically realistic networks supporting cognitive operations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









References
-
- Friederici AD, Singer W. Grounding language processing on basic neurophysiological principles. Trends in cognitive sciences. 2015;19(6):329–38. Epub 2015/04/22. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2015.03.012 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miller KD. Canonical computations of cerebral cortex. Current opinion in neurobiology. 2016;37:75–84. Epub 2016/02/13. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2016.01.008 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPmc4944655. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Treves A. Frontal latching networks: a possible neural basis for infinite recursion. Cognitive neuropsychology. 2005;22(3):276–91. Epub 2005/01/01. doi: 10.1080/02643290442000329 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mountcastle VB. Modality and topographic properties of single neurons of cat's somatic sensory cortex. Journal of neurophysiology. 1957;20(4):408–34. Epub 1957/07/01. . - PubMed
-
- Lubke J, Feldmeyer D. Excitatory signal flow and connectivity in a cortical column: focus on barrel cortex. Brain structure & function. 2007;212(1):3–17. Epub 2007/08/25. doi: 10.1007/s00429-007-0144-2 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

