Evaluation of Hypolipidemic and Antioxidant Effects in Phenolrich Fraction of Crataegus pinnatifida Fruit in Hyperlipidemia Rats and Identification of Chemical Composition by Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadropole Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 29200740
- PMCID: PMC5701418
- DOI: 10.4103/pm.pm_402_16
Evaluation of Hypolipidemic and Antioxidant Effects in Phenolrich Fraction of Crataegus pinnatifida Fruit in Hyperlipidemia Rats and Identification of Chemical Composition by Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadropole Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
Background: Hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) fruit has enjoyed a great popularity as a pleasant-tasting food associated with hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects.
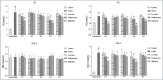
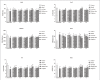
Objective: Our aim was to screen the effective fraction of hawthorn fruit in the treatment of hyperlipidemia rats. Materials and Methods: In this study, ethanol extract of hawthorn fruit (Fr.1) and four fractionated extracts (Fr.2, Fr.3, Fr.4, and Fr.5) were compared to total phenol content evaluated using Folin-Ciocalteu method, and hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects were assessed in hyperlipidemic rats.
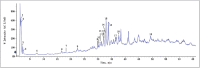
Results: Total phenol content of Fr.4 was higher than other fractions by at least 2 fold. Furthermore, this fraction possessed the strongest hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects in hyperlipidemic rats. On this basis, 15 phenolic compounds and four organic acids in Fr.4 were positively or tentatively identified using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadropole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. In addition, 5-O-caffeoyl quinic acid butyl ester was first reported in hawthorn fruit.
Conclusion: Phenol-rich fraction in hawthorn fruit exhibited satisfactory hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects, and this could be exploited for further promotion of functional foods.
Summary: Phenol-rich fraction in hawthorn fruit possesses most potent hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects in hyperlidemia rats. Abbreviations used: UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS: Ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadropole time-of-flight mass spectrometry; TC: Total cholesterol; TG: Triglyceride; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; GSH-Px: Glutathione peroxidase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; CAT: Catalase; NO: Nitric oxide; NOS: Nitric oxide synthase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; •OOH: Superoxide anions, •OH: Hydroxyl radicals.
Keywords: Antioxidant effect; Crataegus pinnatifida fruit; hypolipidemic effect; phenolic compounds; ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadropole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zhao H, Feng B. Cultivation history. China Fruit-plant Monograph·Hawthorn Flora. Ch II. Beijing, China: Zhongguo Lin Ye Press; 1996.
-
- Qian C, Chen H, Qin R, Lin R, Wu Z, Cui H, et al. Flora of China. Beijing, China: Science Press; 1974.
-
- The Pharmacopoeia Commission of PRC. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Beijing, China: Chemical Industry Press; 2015.
-
- Ling J, Wei B, Lv G, Ji H, Li S. Anti-hyperlipidaemic and antioxidant effects of turmeric oil in hyperlipidaemic rats. Food Chem. 2012;130:229–35.
-
- Belguith-Hadriche O, Bouaziz M, Jamoussi K, Simmonds MS, El Feki A, Makni-Ayedi F. Comparative study on hypocholesterolemic and antioxidant activities of various extracts of fenugreek seeds. Food Chem. 2013;138:1448–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
