Magnetic hydroxyapatite: a promising multifunctional platform for nanomedicine application
- PMID: 29200851
- PMCID: PMC5702531
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S147355
Magnetic hydroxyapatite: a promising multifunctional platform for nanomedicine application
Abstract
In this review, specific attention is paid to the development of nanostructured magnetic hydroxyapatite (MHAp) and its potential application in controlled drug/gene delivery, tissue engineering, magnetic hyperthermia treatment, and the development of contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Both magnetite and hydroxyapatite materials have excellent prospects in nanomedicine with multifunctional therapeutic approaches. To date, many research articles have focused on biomedical applications of nanomaterials because of which it is very difficult to focus on any particular type of nanomaterial. This study is possibly the first effort to emphasize on the comprehensive assessment of MHAp nanostructures for biomedical applications supported with very recent experimental studies. From basic concepts to the real-life applications, the relevant characteristics of magnetic biomaterials are patented which are briefly discussed. The potential therapeutic and diagnostic ability of MHAp-nanostructured materials make them an ideal platform for future nanomedicine. We hope that this advanced review will provide a better understanding of MHAp and its important features to utilize it as a promising material for multifunctional biomedical applications.
Keywords: drug delivery; hydroxyapatite; hyperthermia; iron oxide; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

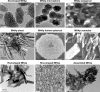
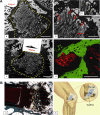
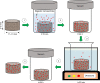
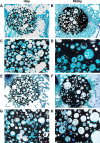



References
-
- Freeman MW, Arrott A, Watson HL. Magnetism in medicine. J Appl Phys. 1960;31:404S–405S.
-
- Pankhurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2003;36:R167–R181.
-
- Polyak B, Friedman G. Magnetic targeting for site-specific drug delivery: applications and clinical potential. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6(1):53–70. - PubMed
-
- Trandafir DL, Mirestean C, Turcu RVF, Frentiu B, Eniu D, Simon S. Structural characterization of nanostructured hydroxyapatite-iron oxide composites. Ceram Int. 2014;40:11071–11078.
-
- Tampieri A, D’Alessandro T, Sandri M, et al. Intrinsic magnetism and hyperthermia in bioactive Fe-doped hydroxyapatite. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(2):843–851. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

