Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and plasticity of the posterior cerebral artery following permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion
- PMID: 29200907
- PMCID: PMC5709481
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.6.643
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and plasticity of the posterior cerebral artery following permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion
Abstract
Vascular dementia (VaD) is a group of heterogeneous diseases with the common feature of cerebral hypoperfusion. To identify key factors contributing to VaD pathophysiology, we performed a detailed comparison of Wistar and Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats subjected to permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAo). Eight-week old male Wistar and SD rats underwent BCCAo, followed by a reference memory test using a five-radial arm maze with tactile cues. Continuous monitoring of cerebral blood flow (CBF) was performed with a laser Doppler perfusion imaging (LDPI) system. A separate cohort of animals was sacrificed for evaluation of the brain vasculature and white matter damage after BCCAo. We found reference memory impairment in Wistar rats, but not in SD rats. Moreover, our LDPI system revealed that Wistar rats had significant hypoperfusion in the brain region supplied by the posterior cerebral artery (PCA). Furthermore, Wistar rats showed more profound CBF reduction in the forebrain region than did SD rats. Post-mortem analysis of brain vasculature demonstrated greater PCA plasticity at all time points after BCCAo in Wistar rats. Finally, we confirmed white matter rarefaction that was only observed in Wistar rats. Our studies show a comprehensive and dynamic CBF status after BCCAo in Wistar rats in addition to severe PCA dolichoectasia, which correlated well with white matter lesion and memory decline.
Keywords: Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion; Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; Dolichoectasia; Sprague-Dawley strain; Vascular dementia; Wistar strain.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

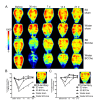

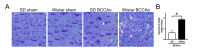
Similar articles
-
The plasticity of posterior communicating artery influences on the outcome of white matter injury induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats.Neurol Res. 2009 Apr;31(3):245-50. doi: 10.1179/174313209X382278. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Neurol Res. 2009. PMID: 19040801
-
White Matter Damage and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration Induced by Permanent Bilateral Occlusion of Common Carotid Artery in the Rat: Comparison between Wistar and Sprague-Dawley Strain.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;12(3):89-94. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.3.89. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 20157400 Free PMC article.
-
A refined model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion resulting in cognitive impairment and a low mortality rate in rats.J Neurosurg. 2018 Sep 7;131(3):892-902. doi: 10.3171/2018.3.JNS172274. Print 2019 Sep 1. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30192196
-
Animal Models of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion: From Mouse to Primate.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 7;20(24):6176. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246176. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31817864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: a model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res Rev. 2007 Apr;54(1):162-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Brain Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 17296232 Review.
Cited by
-
Xinnao Shutong Modulates the Neuronal Plasticity Through Regulation of Microglia/Macrophage Polarization Following Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats.Front Physiol. 2018 May 15;9:529. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00529. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29867570 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrodin Ameliorates Cognitive Dysfunction in Vascular Dementia Rats by Suppressing Ferroptosis via the Regulation of the Nrf2/Keap1-GPx4 Signaling Pathway.Molecules. 2022 Sep 24;27(19):6311. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196311. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234847 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion on the pathology of Alzheimer's disease: A positron emission tomography study in rats.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 1;9(1):14102. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50681-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31575996 Free PMC article.
-
Mumefural Ameliorates Cognitive Impairment in Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion via Regulating the Septohippocampal Cholinergic System and Neuroinflammation.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 13;11(11):2755. doi: 10.3390/nu11112755. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31766248 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture Can Regulate the Peripheral Immune Cell Spectrum and Inflammatory Environment of the Vascular Dementia Rat, and Improve the Cognitive Dysfunction of the Rats.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Jul 19;13:706834. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.706834. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34349636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sopala M, Danysz W. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat enhances age-related deficits in spatial memory. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2001;108:1445–1456. - PubMed
-
- Román GC, Sachdev P, Royall DR, Bullock RA, Orgogozo JM, López-Pousa S, Arizaga R, Wallin A. Vascular cognitive disorder: a new diagnostic category updating vascular cognitive impairment and vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2004;226:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Cho KO, La HO, Cho YJ, Sung KW, Kim SY. Minocycline attenuates white matter damage in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83:285–291. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

