Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and plasticity of the posterior cerebral artery following permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion
- PMID: 29200907
- PMCID: PMC5709481
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.6.643
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and plasticity of the posterior cerebral artery following permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion
Abstract
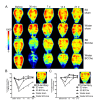
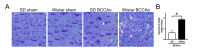
Vascular dementia (VaD) is a group of heterogeneous diseases with the common feature of cerebral hypoperfusion. To identify key factors contributing to VaD pathophysiology, we performed a detailed comparison of Wistar and Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats subjected to permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAo). Eight-week old male Wistar and SD rats underwent BCCAo, followed by a reference memory test using a five-radial arm maze with tactile cues. Continuous monitoring of cerebral blood flow (CBF) was performed with a laser Doppler perfusion imaging (LDPI) system. A separate cohort of animals was sacrificed for evaluation of the brain vasculature and white matter damage after BCCAo. We found reference memory impairment in Wistar rats, but not in SD rats. Moreover, our LDPI system revealed that Wistar rats had significant hypoperfusion in the brain region supplied by the posterior cerebral artery (PCA). Furthermore, Wistar rats showed more profound CBF reduction in the forebrain region than did SD rats. Post-mortem analysis of brain vasculature demonstrated greater PCA plasticity at all time points after BCCAo in Wistar rats. Finally, we confirmed white matter rarefaction that was only observed in Wistar rats. Our studies show a comprehensive and dynamic CBF status after BCCAo in Wistar rats in addition to severe PCA dolichoectasia, which correlated well with white matter lesion and memory decline.
Keywords: Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion; Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; Dolichoectasia; Sprague-Dawley strain; Vascular dementia; Wistar strain.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sopala M, Danysz W. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat enhances age-related deficits in spatial memory. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2001;108:1445–1456. - PubMed
-
- Román GC, Sachdev P, Royall DR, Bullock RA, Orgogozo JM, López-Pousa S, Arizaga R, Wallin A. Vascular cognitive disorder: a new diagnostic category updating vascular cognitive impairment and vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci. 2004;226:81–87. - PubMed
-
- Cho KO, La HO, Cho YJ, Sung KW, Kim SY. Minocycline attenuates white matter damage in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83:285–291. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

