Knowledge, Attitude and Practices (KAP) Regarding Chronic Complications of Diabetes among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Dhaka
- PMID: 29201069
- PMCID: PMC5702002
- DOI: 10.5812/ijem.12555
Knowledge, Attitude and Practices (KAP) Regarding Chronic Complications of Diabetes among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Dhaka
Abstract
Background: To reduce morbidity and mortality, awareness regarding diabetes and its complications is necessary. This study aimed at assessing the level of knowledge, attitude, and practices (KAP) regarding complications of diabetes mellitus among patients with type 2 diabetes in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was carried out recruiting patients with diabetes from the outpatient department of BIRDEM hospital in Dhaka. Overall, 425 patients with diabetes were enrolled in this study. A pretested questionnaire was filled by the interviewer with face to face interview. Levels of KAP were determined by calculating the scores. Multivarable linear regression was used to determine significant predictors for knowledge, attitude, and practices.
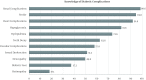
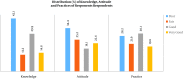
Results: On average, the level of knowledge, attitude, and practices were 9.2 (out of 14), 7.9 (out of 13), and 16.9 (out of 27), respectively. Age and gender were significant predictors of knowledge and attitude. Females had better level of knowledge and attitude compared to males (βs = 0.55 and 1.24, respectively). Patients with graduate degrees and above compared to illiterates reported significantly greater knowledge and practice (βs = 1.27 and 1.44, respectively), after adjustments for covariates. Educational program was the most important significant predictor of KAP. Higher duration of diabetes (β = 0.07) and positive marital status (β = 1.21) had influenced better practice.
Conclusions: Lack of knowledge, poor attitude, and inadequate practice were found in this surveyed communinty. Level of education and educational program on diabetes were the most significant contributing factors. The current study suggests the need of structured educational programs on diabetes and its complications on a regular basis to assist patients in living a productive life.
Keywords: Attitudes; Diabetes Complications; Diabetes Mellitus; Health Knowledge; Practice; Type 2.
Figures
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO . Mortality Database . Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- World Health Organization . Global health estimates: Deaths by cause, age, sex and country. Geneva: WHO; 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources