Docking Studies, Synthesis, and In-vitro Evaluation of Novel Oximes Based on Nitrones as Reactivators of Inhibited Acetylcholinesterase
- PMID: 29201079
- PMCID: PMC5610744
Docking Studies, Synthesis, and In-vitro Evaluation of Novel Oximes Based on Nitrones as Reactivators of Inhibited Acetylcholinesterase
Abstract
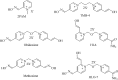
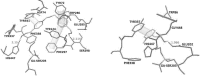
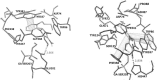
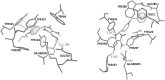
Acetylcholinesterase has important role in synaptic cleft. It breaks down the acetylcholineat cholinergic synapsesand terminates the cholinergic effects. Some chemical agents like organophosphorus compounds (OPCs) including nerve agents and pesticides react with acetylcholinesteraseirreversibly. They inhibit normal biological enzyme action and result in accumulation of acetylcholineand show toxic effects andcholinergic symptoms. The process of Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition can be reversed by a nucleophilic agent to dephosphorylate and reactivate the enzyme. In this study, design and docking studies of 15 novel nitrone based onoximes as reactivators were performed by using AutoDock program. Then, more effective reactivatorsoximes in terms of binding energy and orientation within the active site were synthesized and evaluated in-vitro on human AChE (hAChE) inhibited by paraoxon and compared to standard hAChE reactivators (2-PAM and obidoxime). Our results used to design new derivatives of Oxim with better efficacy than 2-PAM and obidoxime. Syntheses of some selected bis-pyridiniumoximes based on the nitrones are underway.
Keywords: Molecular docking; Nitrones; Organophosphorus compounds; Oximes; Reactivators.
Figures

References
-
- Sussman JL, Harel M, Frolow F, Oefner C, Goldman A, Toker L, Silman I. Atomic structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: a prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science . 1991;253:872–9. - PubMed
-
- Taylor P, Radic Z. The cholinesterases: from genes to proteins. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. . 1994;34:281–320. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjee AK, Marek E, Le HT, Gordon RK. Discovery of non-oximereactivators using an in silicopharmacophore model of oximereactivators of OP-inhibited acetylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. . 2012;49:229–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
