Truncated forms of RUNX3 Unlike Full Length Protein Alter Cell Proliferation in a TGF-β Context Dependent Manner
- PMID: 29201108
- PMCID: PMC5610775
Truncated forms of RUNX3 Unlike Full Length Protein Alter Cell Proliferation in a TGF-β Context Dependent Manner
Abstract
The Runt related transcription factors (RUNX) are recognized as key players in suppressing or promoting tumor growth. RUNX3, a member of this family, is known as a tumor suppressor in many types of cancers, although such a paradigm was challenged by some researchers. The TGF-β pathway governs major upstream signals to activate RUNX3. RUNX3 protein consists of several regions and domains. The Runt domain is a conserved DNA binding domain and is considered as the main part of RUNX proteins. Herein, we compared the effects of Runt domains and full-Runx3 in cell viability by designing two constructs of Runx3, including N-terminal region and Runt domain. We investigated the effect of full-Runx3, N-t, and RD on growth inhibition in AGS, MCF-7, A549, and HEK293 cell lines which are different in TGF-β sensitivity, in the absence and presence of TGF-β. The full length RUNX3 did not notably inhibit growth of these cell lines while, the N-t and RD truncates showed different trends in these cell lines. Cell proliferation in the TGF-β impaired context cell lines (AGS and MCF-7) significantly decrease while in the A549 significantly increase. On the other hand, transfection of N-t and RD did not considerably affect the cell proliferation in the HEK293.Our results show that full-lenght RUNX3 did not affect the cell viability. Conversely, the N-t and RD constructs significantly changed cell proliferation. Therefore, therapeutic potentials for these truncated proteins are suggested in tumors with RUNX proteins dysfunction, even in the TGF-β impair context.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cancer; Domain Analysis; Runt; TGF-β.
Figures

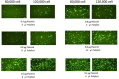

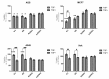
Similar articles
-
Runx3 Expression Inhibits Proliferation and Distinctly Alters mRNA Expression of Bax in AGS and A549 Cancer Cells.Iran J Pharm Res. 2011 Spring;10(2):355-61. Iran J Pharm Res. 2011. PMID: 24250365 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX3 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by reinstating transforming growth factor beta responsiveness in esophageal adenocarcinoma cells.Surgery. 2004 Aug;136(2):310-6. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2004.05.005. Surgery. 2004. PMID: 15300196
-
Tumor suppressor, AT motif binding factor 1 (ATBF1), translocates to the nucleus with runt domain transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) in response to TGF-beta signal transduction.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Jul 23;398(2):321-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.090. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20599712
-
Molecular pathology of RUNX3 in human carcinogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Dec;1796(2):315-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.07.004. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19682550 Review.
-
Tumor suppressor activity of RUNX3.Oncogene. 2004 May 24;23(24):4336-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207286. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15156190 Review.
Cited by
-
RUNX3 is up-regulated in abdominal aortic aneurysm and regulates the function of vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating TGF-β1.J Mol Histol. 2022 Feb;53(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s10735-021-10035-9. Epub 2021 Nov 23. J Mol Histol. 2022. PMID: 34813022
References
-
- Speck NA, Stacy T, Wang Q, North T, Gu T-L, Miller J, Binder M, Marín-Padilla M. Core-binding factor: a central player in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Cancer res. . 1999;59:1789s–93s. - PubMed
-
- Levanon D, Groner Y. Structure and regulated expression of mammalian RUNX genes. Oncogene . 2004;23:4211–9. - PubMed
-
- Blyth K, Cameron ER, Neil JC. The RUNX genes: gain or loss of function in cancer. Nature. Rev. Cancer . 2005;5:376–87. - PubMed
-
- Chuang LS, Ito K, Ito Y. RUNX family: Regulation and diversification of roles through interacting proteins. Int. J. Cancer . 2013;132:1260–71. - PubMed
-
- Kagoshima H, Shigesada K, Satake M, Ito Y, Miyoshi H, Ohki M, Pepling M, Gergen P. The Runt domain identifies a new family of heteromeric transcriptional regulators. Trends. Genet. . 1993;9:338–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
