Whole genome sequencing-based detection of antimicrobial resistance and virulence in non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica isolated from wildlife
- PMID: 29201148
- PMCID: PMC5697165
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-017-0213-x
Whole genome sequencing-based detection of antimicrobial resistance and virulence in non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica isolated from wildlife
Abstract
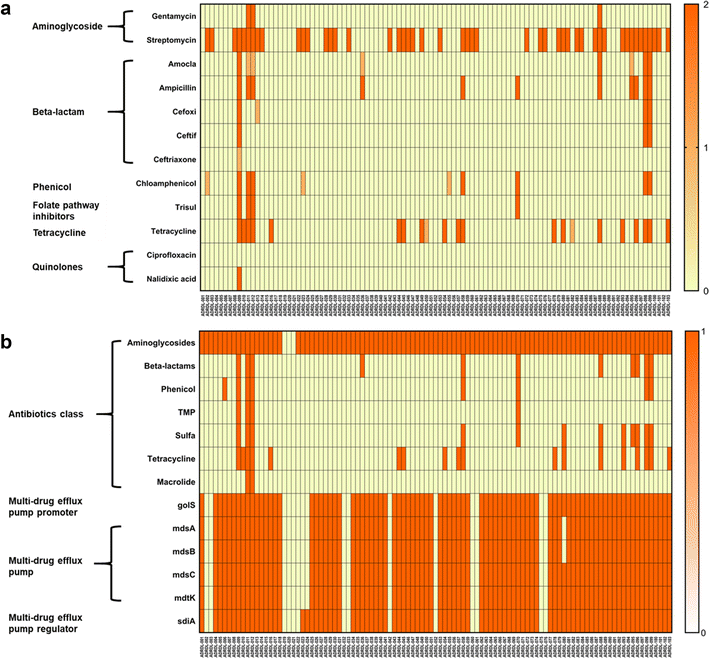
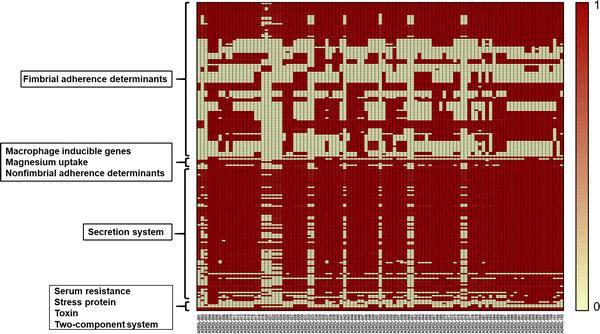
The aim of this study was to generate a reference set of Salmonella enterica genomes isolated from wildlife from the United States and to determine the antimicrobial resistance and virulence gene profile of the isolates from the genome sequence data. We sequenced the whole genomes of 103 Salmonella isolates sampled between 1988 and 2003 from wildlife and exotic pet cases that were submitted to the Oklahoma Animal Disease Diagnostic Laboratory, Stillwater, Oklahoma. Among 103 isolates, 50.48% were from wild birds, 0.9% was from fish, 24.27% each were from reptiles and mammals. 50.48% isolates showed resistance to at least one antibiotic. Resistance against the aminoglycoside streptomycin was most common while 9 isolates were found to be multi-drug resistant having resistance against more than three antibiotics. Determination of virulence gene profile revealed that the genes belonging to csg operons, the fim genes that encode for type 1 fimbriae and the genes belonging to type III secretion system were predominant among the isolates. The universal presence of fimbrial genes and the genes encoded by pathogenicity islands 1-2 among the isolates we report here indicates that these isolates could potentially cause disease in humans. Therefore, the genomes we report here could be a valuable reference point for future traceback investigations when wildlife is considered to be the potential source of human Salmonellosis.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Foodborne pathogen; Salmonella virulence; Salmonellosis; Whole genome sequencing; Wildlife.
Figures
References
-
- Botti V, et al. Salmonella spp. and antibiotic-resistant strains in wild mammals and birds in north-western Italy from 2002 to 2010. Vet Ital. 2013;49(2):195–202. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

