Role of microRNA-26a in the diagnosis of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis in patients with bone trauma
- PMID: 29201216
- PMCID: PMC5704309
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5183
Role of microRNA-26a in the diagnosis of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis in patients with bone trauma
Abstract
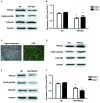
The present study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of action of microRNA (miR)-26a in deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Peripheral blood was collected from 45 patients with DVT and 40 healthy controls. Levels of miR-26a, chemokine C-C motif ligand (CCL)2 mRNA and CCL7 mRNA were detected using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and the value of miR-26a in the clinical diagnosis of DVT was assessed using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. The correlation of miR-26a with CCL2 and CCL7 levels was analyzed using Spearman's rank correlation. In addition, miR-26a and protein kinase C δ (PRKCD) were overexpressed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and PRKCD expression was knocked down by small interfering (si)RNA. Western blotting was conducted to detect the expression of PRKCD and p65. Furthermore, a dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was performed. The results of the current study demonstrated that the expression of miR-26a was significantly downregulated in the peripheral blood of patients with DVT compared with healthy controls (P<0.05) and negatively correlated with CCL2 and CCL7 levels (P<0.05). Furthermore, it was demonstrated that miR-26a markedly inhibited the expression of PRKCD, significantly decreased levels of CCL2 and CCL7 mRNA (P<0.05) and inhibited activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Overexpression of PRKCD in HUVECs inhibited the effects of miR-26a and markedly upregulated the phosphorylation of p65. The present study indicated that miR-26a directly targets PRKCD mRNA and that miR-26a may be a useful biomarker in the clinical diagnosis of DVT. Thus, the present findings suggest that miR-26a regulates the NF-κB signaling pathway by binding to PRKCD mRNA, inhibits the expression of CCL2 and CCL7 and reduces the risk of DVT.
Keywords: clinical diagnosis; deep vein thrombosis; microRNA.
Figures

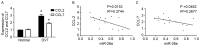

Similar articles
-
Elevated miR-195-5p expression in deep vein thrombosis and mechanism of action in the regulation of vascular endothelial cell physiology.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4617-4624. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8166. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31807149 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol alleviates ox-LDL-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of miR-26a-5p via inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway in human endothelial cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:1783-1789. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.175. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30372882
-
MiR-197-3p affects angiogenesis and inflammation of endothelial cells by targeting CXCR2/COX2 axis.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jul 15;14(7):4666-4677. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35958438 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-26a regulates ANXA1, rather than DAL-1, in the development of lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Apr;15(4):5893-5902. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8048. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29552220 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-26a suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing enhancer of zeste homolog 2.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Jan 6;9:1. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0229-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26733151 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiology of deep vein thrombosis.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Jul;23(3):645-654. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00829-w. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 35471714 Review.
-
MicroRNA-339-5p inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced rat mesangial cells by regulating the Syk/Ras/c-Fos pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Sep;395(9):1075-1085. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02261-z. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35687145
-
Effect of miR-495 on lower extremity deep vein thrombosis through the TLR4 signaling pathway by regulation of IL1R1.Biosci Rep. 2018 Dec 21;38(6):BSR20180598. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180598. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30287499 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNAs in Hemophilia and Thrombosis in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 20;21(10):3598. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103598. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32443696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The protective effects of microRNA-26a in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by repressing EZH2.Cell Cycle. 2020 Mar;19(5):551-566. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1717043. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Cell Cycle. 2020. Update in: Cell Cycle. 2023 Jan;22(1):149. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2151241. PMID: 32054404 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Van der Hulle T, den Exter PL, Planquette B, Meyer G, Soler S, Monreal M, Jiménez D, Portillo AK, O'Connell C, Liebman HA. Risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism and major hemorrhage in cancer-associated incidental pulmonary embolism amongst treated and untreated patients: A pooled analysis of 926 patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:105–113. doi: 10.1111/jth.13172. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cho SY, Youn HJ, Park MY, Shim BJ, Lee SJ, Kim JH, Park JK, Oh CY, Ahn SH, Cho WH. Post-operative multiple thrombosis associated with patent foramen ovale: Embolic stroke, right atrial thrombi, pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2015;23:177–180. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2015.23.3.177. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
