Genetic variation of rs3811463 is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus susceptibility
- PMID: 29201231
- PMCID: PMC5704261
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5188
Genetic variation of rs3811463 is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus susceptibility
Abstract
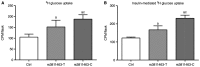
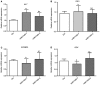
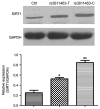
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a growing health concern, and it increases the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes with substantial long-term adverse health impacts on mothers and their offspring. Several studies have revealed specific associations between genetic variants and the risk of GDM. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the major type of genetic variation in humans. Let-7 microRNA targets are enriched for genes containing SNPs associated with glucose metabolism, including Lin28. In the present study, the effect of T/C variants of rs3811463 (a SNP located near to the let-7 binding site in Lin28) on GDM risk was investigated. A GDM rat model was successfully constructed using a high fat diet and streptozotocin injection, and the primary skeletal muscle cells were isolated. The cell transfection results demonstrated that rs3811463-T/C significantly affected the glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis indicated that the C allele at rs3811463 regulated the expression of glucose metabolism-associated genes insulin-like growth factor two binding protein 2 and glucokinase. Western blot analysis data revealed that replacement of the T allele by the C allele at rs3811463 modulated the protein level of Sirtuin 1. Taken together, it was concluded that the let-7/Lin28 axis regulated glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity by modulating the expression of glucose metabolism-associated proteins. These findings provide novel evidence on the association between genetic variations of rs3811463 and GDM susceptibility.
Keywords: Lethal-7; Lin28; gestational diabetes; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
