A novel effective chemical hemin for the treatment of acute carbon monoxide poisoning in mice
- PMID: 29201235
- PMCID: PMC5704266
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5157
A novel effective chemical hemin for the treatment of acute carbon monoxide poisoning in mice
Abstract
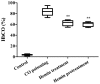
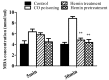
There is no effective drug for the therapy of acute carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the potential preventive and therapeutic effects of hemin on an animal model of acute CO poisoning and to provide a potential therapeutic candidate drug. A total of 80 Kunming mice were randomly divided into four groups, namely the air control, acute CO poisoning, hemin-treatment + CO and hemin-pretreatment + CO groups (n=20 each). Furthermore, the mortality rate of mice, blood carboxyhaemoglobin (HbCO) concentration and serum malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration were measured, and pathological changes of the hippocampal area were determined using histochemical staining. The mice with acute CO poisoning had a 50% mortality rate at 1 h, with an increase in blood HbCO, serum MDA levels and pathological impairments of the hippocampus. Furthermore, the mortality rate, blood HbCO and serum MDA levels of mice with pretreatment and treatment of hemin were decreased. Additionally, the pathological changes of the hippocampal area were improved in the hemin-treatment and hemin-pretreatment groups compared with the mice treated with CO. These results suggest that hemin is a novel effective chemical for the prevention and treatment of acute CO poisoning in mice. Therefore, the present study provides a novel method and experimental basis for the application of hemin in treating patients with acute CO poisoning.
Keywords: acute carbon monoxide poisoning; animal model; carboxyhaemoglobin; hemin; oxidative stress.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
