Antihypertensive Effects of Roselle-Olive Combination in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 29201276
- PMCID: PMC5671754
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9460653
Antihypertensive Effects of Roselle-Olive Combination in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
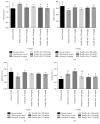
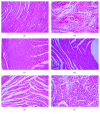
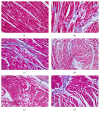
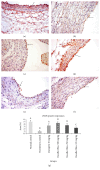
This study aimed to evaluate the antihypertensive efficacy of a new combination therapy of Hibiscus sabdariffa and Olea europaea extracts (2 : 1; Roselle-Olive), using N(G)-nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester- (L-NAME-) induced hypertensive model. Rats received L-NAME (50 mg/kg/day, orally) for 4 weeks. Concurrent treatment with Roselle-Olive (500, 250, and 125 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks) resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, reversed the L-NAME-induced suppression in serum nitric oxide (NO), and improved liver and kidney markers, lipid profile, and oxidative status. Furthermore, Roselle-Olive significantly lowered the elevated angiotensin-converting enzyme activity (ACE) and showed a marked genoprotective effect against oxidative DNA damage in hypertensive rats. Roselle-Olive ameliorated kidney and heart lesions and reduced aortic media thickness. Real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry showed an enhanced endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene and protein expression in both heart and kidney of Roselle-Olive-treated rats. To conclude, our data revealed that Roselle-Olive is an effective combination in which H. sabdariffa and O. europaea synergistically act to control hypertension. These effects are likely to be mediated by antioxidant and genoprotective actions, ACE inhibition, and eNOS upregulation by Roselle-Olive constituents. These findings provide evidences that Roselle-Olive combination affords efficient antihypertensive effect with a broad end-organ protective influence.
Figures









References
-
- Jing P., Qian B., He Y., et al. Screening milk-derived antihypertensive peptides using quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) modelling and in vitro/in vivo studies on their bioactivity. International Dairy Journal. 2014;35(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2013.10.009. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

