Vitrification of Mouse MII Oocyte Decreases the Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number, TFAM Gene Expression and Mitochondrial Enzyme Activity
- PMID: 29201664
- PMCID: PMC5691250
Vitrification of Mouse MII Oocyte Decreases the Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number, TFAM Gene Expression and Mitochondrial Enzyme Activity
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was determination of the changes in the reactive oxygen species (ROS) level, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number and enzyme activity and transcription factor A (TFAM) gene expression in oocytes after vitrification.
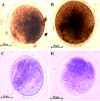
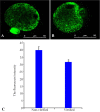
Methods: The oocytes at metaphase II (MII) stage (n=320) were collected from super-ovulated adult female mice (n=40). These oocytes were divided into vitrified and non-vitrified groups (n=160 in each group). After vitrification of oocytes, ROS level, mtDNA copy number; TFAM gene expression and mitochondrial enzymes activity (cytochrome C oxidase and succinate dehydrogenase) were assessed and compared with non-vitrified group. Visualization of the mitochondria was done using Mitotracker green staining under confocal microscope. Data were compared by independent T-test. Values of p<0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
Results: The survival rate of oocytes after vitrification and warming was 96.05%. The intensity of cytochrome C oxidase activity, mtDNA copy number and TFAM gene expression in non-vitrified oocytes were significantly lower and the level of ROS was higher in vitrified oocytes in comparison with non-vitrified group (p<0.05). But the intensity of succinate dehydrogenase activity was not significantly different between the two groups. The pattern of mitochondrial distribution in two groups of study was similar but the intensity of Mitotracker green in non-vitrified oocytes was significantly higher than vitrified oocytes (p<0.05).
Conclusion: This study showed that vitrification of mouse MII oocytes reduced the mtDNA copy number and mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase activity by increasing ROS level, thus the subsequent embryo development may be affected.
Keywords: Cytochrome c oxidase; Reactive oxygen species; Succinate dehydrogenase; mtDNA copy number.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Winkler-Crepaz K, Böttcher B, Toth B, Wildt L, Hofer-Tollinger S. What is new in 2017? Update on fertility preservation in cancer patients. Minerva Endocrinol. 2017;42(4):331–9. - PubMed
-
- Goldman RH, Racowsky C, Farland LV, Munné S, Ribustello L, Fox JH. Predicting the likelihood of live birth for elective oocyte cryopreservation: a counseling tool for physicians and patients. Hum Reprod. 2017;32(4):853–9. - PubMed
-
- Liu M, Zhou W, Chu D, Fu L, Sha W, Liu S, et al. A modified vitrification method reduces spindle and chromosome abnormalities. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2017;63(3):199–205. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
