Histopathological Assessment of Dyspepsia in the Absence of Endoscopic Mucosal Lesions
- PMID: 29201738
- PMCID: PMC5578574
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1178
Histopathological Assessment of Dyspepsia in the Absence of Endoscopic Mucosal Lesions
Abstract
Introduction: Dyspepsia is a common symptom with an extensive differential diagnosis. Endoscopy alone may miss serious mucosal lesions in about 15 to 30% of cases. The aim was to determine histopathological features of gastric and duodenal mucosal biopsies in patients with dyspepsia and normal looking upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy.
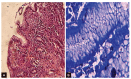
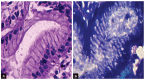
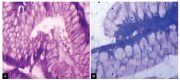
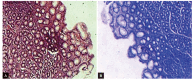
Materials and methods: One hundred and five adult patients presenting with dyspepsia with no endoscopic mucosal lesions in the upper GI tract were included. Gastric biopsy specimens according to Sydney-Houston system for grading gastritis and biopsy from duodenum were taken. The histopathological features were graded according to the Sydney-Houston system classification for grading gastritis.
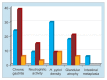
Results: The histological lesions were found in 65.7% (69 out of 105 endoscopy free dyspeptic patients). Chronic inflammation was the commonest finding. Neutrophilic activity, glandular atrophy, and mild degree of intestinal metaplasia were present in 27, 45, and 6 patients (22.8, 42.8, and 5.7% respectively). Helicobacter pylori was present in 54 patients with histopathological lesions and in 6 patients without histopathological lesions, and the difference was significant (p = 0.045).
Conclusion: The endoscopic diagnosis of dyspepsia correlated poorly with histopathological findings. The histopathological examination allowed detection and grading of gastric pathology in dyspepsia with normal endoscopy and the commonest finding was the moderate chronic gastritis.
How to cite this article: Dawod HM, Emara MW. Histopathological Assessment of Dyspepsia in the Absence of Endoscopic Mucosal Lesions. Euroasian J Hepato-Gastroenterol 2016;6(2):97-102.
Keywords: Biopsy; Chronic gastritis; Dyspepsia; Endoscopy..
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Endoscopic and histopathological findings of the upper gastrointestinal tract in patients with functional and organic dyspepsia].Przegl Lek. 2014;71(4):204-9. Przegl Lek. 2014. PMID: 25141579 Polish.
-
A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study on the Histopathology of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Endoscopic Biopsy in Dyspeptic Patients.Cureus. 2024 May 2;16(5):e59508. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59508. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38826983 Free PMC article.
-
[Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer precursor lesions in patients with dyspepsia].Arq Gastroenterol. 2007 Apr-Jun;44(2):93-8. doi: 10.1590/s0004-28032007000200002. Arq Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17962851 Portuguese.
-
Gastroduodenal lesions and Helicobacter pylori infection in hemodialysis patients.Saudi Med J. 2004 Aug;25(8):1010-4. Saudi Med J. 2004. PMID: 15322589
-
Gastric Epithelial Polyps: Current Diagnosis, Management, and Endoscopic Frontiers.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 8;16(22):3771. doi: 10.3390/cancers16223771. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39594726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of risks of gastric cancer by gastric mucosa among Indonesian ethnic groups.PLoS One. 2019 May 9;14(5):e0216670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216670. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31071187 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective study for evaluating the effect of gastric targeted biopsy sampling with I-scan optical enhancement on the diagnostic yield of CLOtest for Helicobacter pylori infection.Health Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 22;5(3):e621. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.621. eCollection 2022 May. Health Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35509392 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of endoscopic findings, histopathological features and Helicobacter pylori infection in adult dyspeptic patients from the cold desert tribal region of Spiti Valley, Himachal Pradesh.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 4. doi: 10.1007/s12664-025-01816-1. Online ahead of print. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40613854
-
Demographic, Endoscopic and Histopathologic Features Among Stool H. pylori Positive and Stool H. pylori Negative Patients With Dyspepsia.Gastroenterology Res. 2017 Oct;10(5):305-310. doi: 10.14740/gr886w. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Gastroenterology Res. 2017. PMID: 29118872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conoroy RT. Siddiqi. B. Dyspepsia. Prim Care. 2007 Mar;34(1):99–108. - PubMed
-
- Talley NJ, Vakil NB, Moayyedi P. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the evaluation of dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 2005 Nov;129(5):1756–1780. - PubMed
-
- Drossman DA. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterology. 2006 Apr;130(5):1377–1390. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman D, Fennerty MB, Morris CD, Holub J, Eisen G, Sonnenberg A. Endoscopic evaluation of patients with dyspepsia: results from the national endoscopic data repository. Gastroenterology. 2004 Oct;127(4):106–775. - PubMed
-
- Bytzer P. Dyspepsia. Ann Intern Med. 2001 May;134(9 Pt 2):815. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
