Effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Versus Intra-articular Injections of Hyaluronic Acid for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 29201822
- PMCID: PMC5698670
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.5.828
Effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Versus Intra-articular Injections of Hyaluronic Acid for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate and compare the effects and outcomes of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) and intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid (HA) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA).
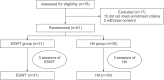
Methods: Of the 78 patients recruited for the study, 61 patients met the inclusion criteria. The enrolled patients were randomly divided into two groups: the ESWT group and the HA group. The ESWT group underwent 3 sessions of 1,000 shockwave pulses performed on the affected knee with the dosage adjusted to 0.05 mJ/mm2 energy. The HA group was administered intra-articular HA once a week for 3 weeks with a 1-week interval between each treatment. The results were measured with the visual analogue scale (VAS), Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC), Lequesne index, 40-m fast-paced walk test, and stair-climb test (SCT). A baseline for each test was measured before treatment and then the effects of the treatments were measured by each test at 1 and 3 months after treatment.
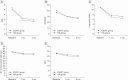
Results: In both groups, the scores of the VAS, WOMAC, Lequesne index, 40-m fast-paced walk test, and SCT were significantly improved in a time-dependent manner (p<0.01). There were no statistically significant differences measured at 1 and 3 months after treatment between the two groups (p>0.05).
Conclusion: The ESWT can be an alternative treatment to reduce pain and improve physical functions in patients with knee OA.
Keywords: High-energy shock waves; Hyaluronic acid; Knee osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on "Effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Versus Intra-articular Injections of Hyaluronic Acid for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis".Ann Rehabil Med. 2018 Apr;42(2):372-373. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.2.372. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Ann Rehabil Med. 2018. PMID: 29766987 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G, Abramson S, Altman RD, Arden N, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence-based, expert consensus guidelines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16:137–162. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen C, Lefevre-Colau MM, Poiraudeau S, Rannou F. Evidence and recommendations for use of intra-articular injections for knee osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59:184–189. - PubMed
-
- Sofat N, Ejindu V, Kiely P. What makes osteoarthritis painful? The evidence for local and central pain processing. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2011;50:2157–2165. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

