The Scope of Big Data in One Medicine: Unprecedented Opportunities and Challenges
- PMID: 29201868
- PMCID: PMC5696324
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00194
The Scope of Big Data in One Medicine: Unprecedented Opportunities and Challenges
Abstract
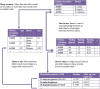
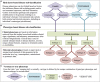
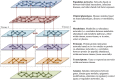
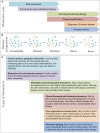
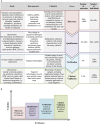
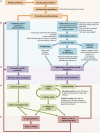
Advances in high-throughput molecular biology and electronic health records (EHR), coupled with increasing computer capabilities have resulted in an increased interest in the use of big data in health care. Big data require collection and analysis of data at an unprecedented scale and represents a paradigm shift in health care, offering (1) the capacity to generate new knowledge more quickly than traditional scientific approaches; (2) unbiased collection and analysis of data; and (3) a holistic understanding of biology and pathophysiology. Big data promises more personalized and precision medicine for patients with improved accuracy and earlier diagnosis, and therapy tailored to an individual's unique combination of genes, environmental risk, and precise disease phenotype. This promise comes from data collected from numerous sources, ranging from molecules to cells, to tissues, to individuals and populations-and the integration of these data into networks that improve understanding of heath and disease. Big data-driven science should play a role in propelling comparative medicine and "one medicine" (i.e., the shared physiology, pathophysiology, and disease risk factors across species) forward. Merging of data from EHR across institutions will give access to patient data on a scale previously unimaginable, allowing for precise phenotype definition and objective evaluation of risk factors and response to therapy. High-throughput molecular data will give insight into previously unexplored molecular pathophysiology and disease etiology. Investigation and integration of big data from a variety of sources will result in stronger parallels drawn at the molecular level between human and animal disease, allow for predictive modeling of infectious disease and identification of key areas of intervention, and facilitate step-changes in our understanding of disease that can make a substantial impact on animal and human health. However, the use of big data comes with significant challenges. Here we explore the scope of "big data," including its opportunities, its limitations, and what is needed capitalize on big data in one medicine.
Keywords: bioinformatics; clinical informatics; deep phenotyping; environmental epidemiology; genetic epidemiology; multilayer disease module; network medicine; structural informatics.
Figures

References
-
- Sagiroglu S, Sinanc D. Big data: a review. 2013 International Conference on Collaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS) San Diego, CA: IEEE (2013). p. 42–7.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

