Treatment Outcomes of 257 Patients with Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treated with Nimotuzumab Plus Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy with or without Chemotherapy: A Single-Institution Experience
- PMID: 29202278
- PMCID: PMC5723380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2017.11.002
Treatment Outcomes of 257 Patients with Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treated with Nimotuzumab Plus Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy with or without Chemotherapy: A Single-Institution Experience
Abstract
Objectives: To report the long-term outcome and toxicity of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (LA NPC) treated with nimotuzumab (h-R3) plus intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) with or without chemotherapy.
Methods: From May 2008 to March 2014, 3022 newly histology-proven, nonmetastatic NPC patients were retrospectively reviewed; among them, 257 patients treated with h-R3 were enrolled in this study. The patients' age range was between 10 and 76 years. The distribution of patients by disease stage was 150 (58.4%) in stage III, 88 (34.2%) in stage IV A, and 19 (7.4%) in stage IV B. All the patients received the treatment of h-R3 plus IMRT, and from them, 239 cases were also treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Acute and late radiation-related toxicities were graded according to the Acute and Late Radiation Morbidity Scoring Criteria of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. The accumulated survival was calculated according to the Kaplan-Meier method. Log-rank test was used to compare the survival difference. Multivariate analysis was performed using Cox's proportional-hazard model.
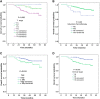
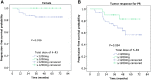
Results: All 257 patients had completed combined treatment; 231 patients received h-R3 plus IMRT with induction chemotherapy (IC), while 26 patients received only h-R3 plus IMRT. With a median follow-up of 48 months (range, 13-75 months), the estimated 5-year local recurrence-free survival, regional recurrence-free survival, distant metastases-free survival, progression-free survival, and overall survival (OS) rates were 94.3%, 94.8%, 91.9%, 83.4%, and 86.2%, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that age, T stage, clinical stage, and IC were related with OS. Multivariate analysis indicated that T stage and IC were independent prognostic factors for OS. The incidence of grade 3 to 4 acute mucositis and leukocytopenia was 10.9% and 19.8%, respectively, with no cases of skin rash and infusion reaction. Xerostomia was the most common late complication, and the degree of dry mouth in most survivors was mild to moderate at the last follow-up time.
Conclusion: h-R3 plus IMRT with or without chemotherapy showed promising outcomes in terms of locoregional control and survival without increasing the incidence of radiation-related toxicities for patients.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-Term Use of Nimotuzumab in Combination With Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Experience of a Single Institution.Oncol Res. 2018 Mar 5;26(2):277-287. doi: 10.3727/096504017X15079846743590. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 29046165 Free PMC article.
-
Experience with combination of nimotuzumab and intensity-modulated radiotherapy in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Nov 18;8:3383-90. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S93238. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26604795 Free PMC article.
-
Survival without concurrent chemotherapy for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with induction chemotherapy plus intensity-modulated radiotherapy: Single-center experience from an endemic area.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(51):e18484. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018484. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31861031 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy plus adjuvant chemotherapy for the treatment of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective controlled study.Chin J Cancer. 2016 Jan 6;35:2. doi: 10.1186/s40880-015-0076-9. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26739148 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of intensity-modulated radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy or surgery in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head-and-neck.Biologics. 2013;7:223-9. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S48664. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Biologics. 2013. PMID: 24204121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction chemotherapy plus nimotuzumab followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy for advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Jul 17;17(5):1317-1324. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.86712. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 34522261 Free PMC article.
-
Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report.Open Life Sci. 2025 Jul 11;20(1):20251134. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1134. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40667483 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Response Prediction of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Based on Histogram Analysis of Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Feb;40(2):326-333. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5925. Epub 2019 Jan 10. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 30630832 Free PMC article.
-
Young oncologists benefit more than experts from deep learning-based organs-at-risk contouring modeling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy: A multi-institution clinical study exploring working experience and institute group style factor.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 May 8;41:100635. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100635. eCollection 2023 Jul. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37251619 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Combined PD-1 Inhibitor With Induction Chemotherapy Followed by IMRT Plus Nimotuzumab in Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2025 Feb 26;18:283-296. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S503674. eCollection 2025. Onco Targets Ther. 2025. PMID: 40017718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–132. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lorlet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard P, Lee A, Marguet S, Ledlercq J, Ng WT, Ma J, Chan AT, Huang PY, Benhamou E, Zhu G. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an update of the MAC-NPC meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(6):645–655. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

