Posterior intervertebral space debridement, annular bone grafting and instrumentation for treatment of lumbosacral tuberculosis
- PMID: 29202743
- PMCID: PMC5716235
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-017-0310-2
Posterior intervertebral space debridement, annular bone grafting and instrumentation for treatment of lumbosacral tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: The choice of surgical methods for lumbosacral tuberculosis is controversial due to the complex anterior anatomy and peculiar biomechanics of the lumbosacral junction. The objective of this study was to explore the clinical effect of posterior intervertebral space debridement with annular bone graft fusion and fixation for the treatment of lumbosacral tuberculosis.
Methods: We retrospectively analysed data from 23 patients with lumbosacral tuberculosis who had undergone posterior intervertebral space debridement with annular bone fusion and fixation between January 2008 and September 2014. The mean age of the patients was 49.0 years (range, 27-71), and the mean duration of disease until treatment was 10.2 months (range, 6-20). The lumbosacral angle, visual analogue scale (VAS) score, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP) level, American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) grade and Social Functioning-36 (SF-36) score were determined to ascertain the clinical effects of the treatment.
Results: All patients underwent follow-up observation. The mean follow-up time was 34.2 months (range, 18-45), the mean operation time was 167.0 min (range, 130-210) and the mean blood loss was 767.4 ml (range, 500-1150). The lumbosacral angle was 21.0° ± 2.1° before operation, rising to 28.8° ± 1.7° after operation (p < 0.05) and being maintained thereafter. The mean VAS score before operation was 8.1 ± 0.6, decreasing to 1.2 ± 0.5 (p < 0.05) at the final follow-up. The mean ESR and CRP values were 49.1 ± 5.6 mm and 64.9 ± 11.9 mg/L, respectively, before operation, decreasing to normal at the final follow-up. The preoperative ASIA grade was C in 6 patients, D in 12 and E in 5. At the final follow-up, all patients had an ASIA grade of E except for one patient with a grade of D. For all patients, the SF-36 score at the final follow-up was higher than the preoperative and postoperative scores.
Conclusions: Posterior intervertebral space debridement with annular bone graft fusion and fixation is an effective treatment for lumbosacral spine tuberculosis.
Keywords: Bone graft; Fixation; Fusion; Intervertebral space debridement; Posterior.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of the Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital was obtained for this study. Each author certifies that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles.
Consent for publication
All patients signed informed consent forms to publish their personal details in this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
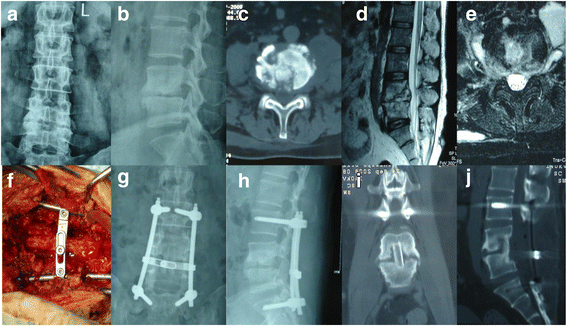
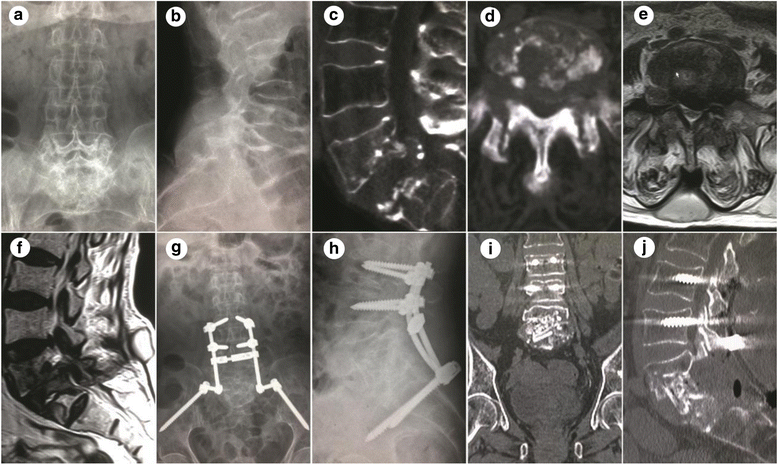
Similar articles
-
Unilateral Limited Laminectomy for Debridement to Treat Localized Short-Segment Lumbosacral Spinal Tuberculosis: A Retrospective Case Series.Orthop Surg. 2021 Jun;13(4):1170-1180. doi: 10.1111/os.12940. Epub 2021 May 4. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33942987 Free PMC article.
-
[Posterior debridement and bone grafting via intervertebral space combined with internal fixation for the treatment of lumbosacral tuberculosis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2017 Feb 25;30(2):137-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2017.02.009. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2017. PMID: 29350004 Chinese.
-
[One-stage posterior debridement combined with lumbar-ilium fixation and bone graft fusion for the treatment of lumbosacral tuberculosis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020 Feb 25;33(2):166-72. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2020.02.015. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020. PMID: 32133818 Chinese.
-
One-stage posterior debridement approach combined with autogenous bone grafting and internal fixation for the treatment of adult thoracic or lumbar suppurative spondylitis via the multifidus and longissimus interspaces.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Apr 1;20(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05735-x. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40170183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis: an updated review.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Dec 18;29(1):588. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02198-4. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39695719 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Application of one-stage posterior surgery via unilateral musculussacrospinalis iliac flap approach in treatment of lumbosacral tuberculosis].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Mar 15;33(3):296-301. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201809090. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30874384 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Medium-Term Follow-Up Outcomes of One-Stage Posterior Lumbosacral or Lumbopelvic Fixation in the Management of Lumbosacral Junction Tuberculosis in Adults.Orthop Surg. 2021 Oct;13(7):2051-2060. doi: 10.1111/os.13150. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 34590777 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Outcomes in Spinal Tuberculosis: A Review of the Literature.Asian Spine J. 2021 Jun;15(3):381-391. doi: 10.31616/asj.2020.0086. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Asian Spine J. 2021. PMID: 32951405 Free PMC article.
-
Unilateral Limited Laminectomy for Debridement to Treat Localized Short-Segment Lumbosacral Spinal Tuberculosis: A Retrospective Case Series.Orthop Surg. 2021 Jun;13(4):1170-1180. doi: 10.1111/os.12940. Epub 2021 May 4. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33942987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bezer M, Kucukdurmaz F, Aydin N, Kocaoglu B, Guven O. Tuberculous spondylitis of the lumbosacral region: long-term follow-up of patients treated by chemotherapy, transpedicular drainage, posterior instrumentation, and fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18:425–429. doi: 10.1097/01.bsd.0000171627.11171.6f. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Talu U, Gogus A, Ozturk C, Hamzaoglu A, Domanic U. The role of posterior instrumentation and fusion after anterior radical debridement and fusion in the surgical treatment of spinal TB: experience of 127 cases. J Spinal Disord. 2006;19:554–559. doi: 10.1097/01.bsd.0000211202.93125.c7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yaldz C, Özdemir N, Yaman O, Feran HG, Tansug T, Minoglu M. A retrospective study of 39 patients treated with anterior approach of thoracic and lumbar spondylodiscitis: clinical manifestations, anterior surgical treatment, and outcome. Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e2110. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

