Genistein induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells by reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal via a Notch1/NF-κB/slug/E-cadherin pathway
- PMID: 29202800
- PMCID: PMC5715491
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3829-9
Genistein induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells by reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal via a Notch1/NF-κB/slug/E-cadherin pathway
Abstract
Background: Genistein has been known to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in several kinds of cancer cells. While knowledge of genistein in regulating epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) of colon cancer cells is unknown.
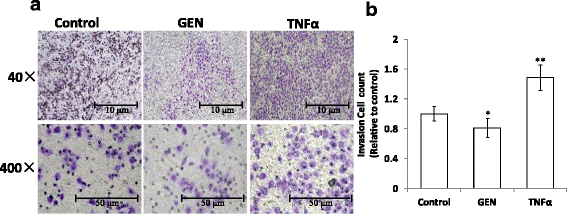
Methods: To investigate the effects and mechanisms of genistein on EMT of colon cancer cells, HT-29 cells were used and treated by genistein and TNF-α in this paper. EMT was determined by cell invasion assays using a transwell chamber and the expression changes of EMT-related markers were confirmed by RT-PCR, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence staining.
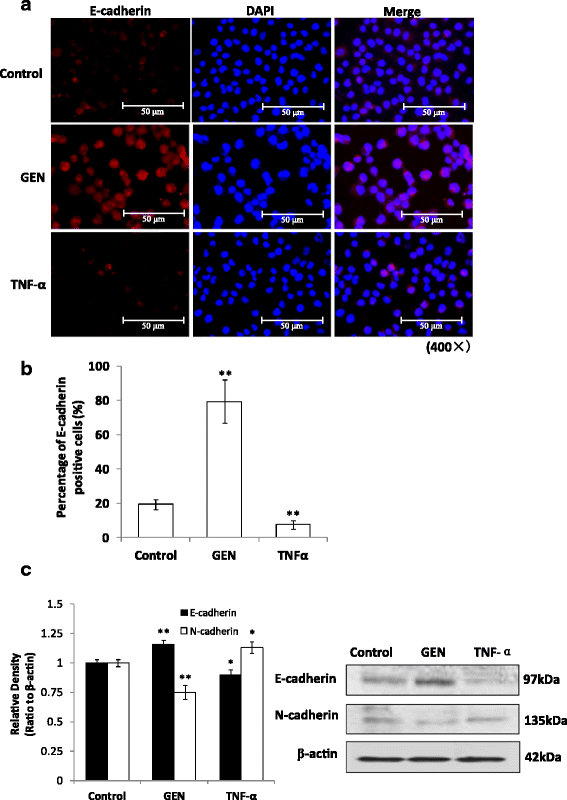
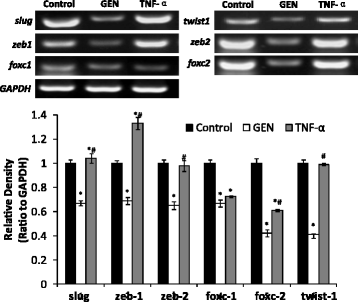
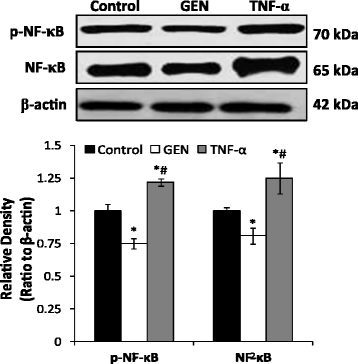
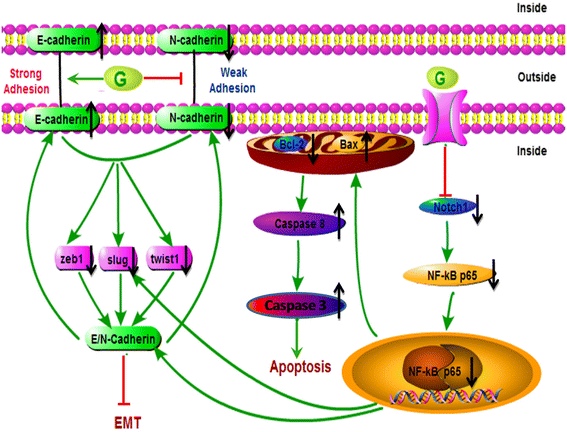
Results: Genistein inhibited cell migration at 200 μmol/L. Genistein reversed the EMT of colon cancer cells by upregulation of E-cadherin and downregulation of N-cadherin, accompanied by the suppression of EMT related makers, such as Snail2/slug, ZEB1, ZEB2, FOXC1, FOXC2 and TWIST1. Moreover, genistein can inhibit the expression of notch-1, p-NF-κB and NF-κB, while promote the expression of Bax/Bcl-2 and caspase-3 in HT-29 cells.
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that genistein suppressed the migration of colon cancer cells by reversal the EMT via suppressing the Notch1/NF-κB/slug/E-cadherin pathway. Genistein may be developed as a potential antimetastasis agent to colon cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Colon cancer cell; Epithelial mesenchymal transition; Genistein.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experiments in this paper have no animal and human beings were included. And the study received local approval of the Ethic Committee of Academy of State Administration of Grain.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Osthole inhibited TGF β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by suppressing NF-κB mediated Snail activation in lung cancer A549 cells.Cell Adh Migr. 2017 Sep 3;11(5-6):464-475. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1259058. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2017. PMID: 28146373 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human colon cancer cells through NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 14;39(5):BSR20190452. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190452. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30967496 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 14;21(34):9887-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9887. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26379394 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Dietary Phytoestrogens on the Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Diverse Cancer Metastasis.Toxins (Basel). 2016 May 24;8(6):162. doi: 10.3390/toxins8060162. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27231938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The activated NF-kappaB-Snail-RKIP circuitry in cancer regulates both the metastatic cascade and resistance to apoptosis by cytotoxic drugs.Crit Rev Immunol. 2009;29(3):241-54. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i3.40. Crit Rev Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19538137 Review.
Cited by
-
F. Nucleatum enhances oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation via E-cadherin/β-Catenin pathway.BMC Oral Health. 2024 May 2;24(1):518. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04252-3. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38698370 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic Metabolism of Flavonoids by Gut Microbiota and Its Impact on Gastrointestinal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 4;13(16):3934. doi: 10.3390/cancers13163934. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition and potential treatment of colorectal cancer by natural compounds via various signaling pathways.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 8;12:956793. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.956793. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36158694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genistein: Therapeutic and Preventive Effects, Mechanisms, and Clinical Application in Digestive Tract Tumor.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 29;2022:5957378. doi: 10.1155/2022/5957378. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35815271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genistein suppresses microglial activation and inhibits apoptosis in different brain regions of hypoxia-exposed mice model of amnesia.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Oct;37(7):2521-2532. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01039-9. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35895244
References
-
- Wang Z, et al. Genistein increases gene expression by demethylation of WNT5a promoter in colon cancer cell line SW1116. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(11):4537–4545. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

