PA5470 Counteracts Antimicrobial Effect of Azithromycin by Releasing Stalled Ribosome in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 29203495
- PMCID: PMC5786749
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01867-17
PA5470 Counteracts Antimicrobial Effect of Azithromycin by Releasing Stalled Ribosome in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
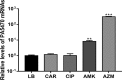
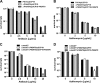
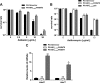
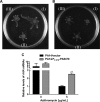
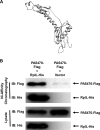
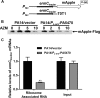
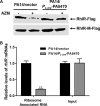
Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes various acute and chronic infections in humans. Treatment with azithromycin (AZM) has been shown to benefit patients with chronic P. aeruginosa infections. By binding to the exit tunnel of the 50S ribosome, AZM causes ribosome stalling and depletion of the intracellular tRNA pool. It has been shown that AZM is able to kill stationary-phase P. aeruginosa cells and repress quorum sensing-regulated virulence factors as well as swarming motility. In P. aeruginosa, the PA5470 gene encodes a putative peptide chain release factor whose expression is highly induced by macrolide antibiotics. However, its function remains unknown. Here, we found that overexpression of PA5470 increased bacterial tolerance against AZM and alleviated the repression of swarming motility. Ribosome pulldown assays revealed that PA5470 contributes to the release of ribosome stalled by AZM. We further demonstrate that overexpression of PA5470 counteracts AZM-mediated repression of the translation of the quorum sensing regulator RhlR. Overall, our results revealed a novel role of PA5470 in the bacterial response to AZM.
Keywords: PA5470; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antibiotic resistance; azithromycin.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Azithromycin blocks quorum sensing and alginate polymer formation and increases the sensitivity to serum and stationary-growth-phase killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and attenuates chronic P. aeruginosa lung infection in Cftr(-/-) mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Oct;51(10):3677-87. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01011-06. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17620382 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Activity of Berberine with Azithromycin against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated from Patients with Cystic Fibrosis of Lung In Vitro and In Vivo.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1657-1669. doi: 10.1159/000479411. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28738346
-
Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by azithromycin and its effectiveness in urinary tract infections.J Med Microbiol. 2011 Mar;60(Pt 3):300-306. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.025387-0. Epub 2010 Dec 2. J Med Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21127154
-
Central role of quorum sensing in regulating the production of pathogenicity factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Future Microbiol. 2008 Feb;3(1):97-106. doi: 10.2217/17460913.3.1.97. Future Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18230038 Review.
-
Targeting quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: current and emerging inhibitors.Future Microbiol. 2013 Jul;8(7):901-21. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.57. Future Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23841636 Review.
Cited by
-
Azithromycin represses evolution of ceftazidime/avibactam resistance by translational repression of rpoS in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Bacteriol. 2025 May 22;207(5):e0055224. doi: 10.1128/jb.00552-24. Epub 2025 Apr 30. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40304512 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Polynucleotide Phosphorylase Controls Tolerance to Aminoglycoside Antibiotics by Regulating the MexXY Multidrug Efflux Pump.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Jan 20;65(2):e01846-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01846-20. Print 2021 Jan 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33257447 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Control Mechanisms in Bacterial Translation.Acta Naturae. 2021 Apr-Jun;13(2):32-44. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11401. Acta Naturae. 2021. PMID: 34377554 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive Responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Treatment with Antibiotics.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Jan 18;66(1):e0087821. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00878-21. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34748386 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of ArmZ with the DNA-binding domain of MexZ induces expression of mexXY multidrug efflux pump genes and antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 9;63(12):e01199-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01199-19. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31527038 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

