Three distinct developmental pathways for adaptive and two IFN-γ-producing γδ T subsets in adult thymus
- PMID: 29203769
- PMCID: PMC5715069
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01963-w
Three distinct developmental pathways for adaptive and two IFN-γ-producing γδ T subsets in adult thymus
Abstract
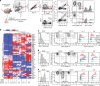
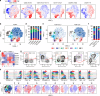
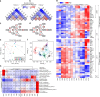
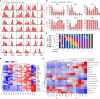
Murine γδ T cells include subsets that are programmed for distinct effector functions during their development in the thymus. Under pathological conditions, different γδ T cell subsets can be protective or can exacerbate a disease. Here we show that CD117, CD200 and CD371, together with other markers, identify seven developmental stages of γδ T cells. These seven stages can be divided into three distinct developmental pathways that are enriched for different TCRδ repertoires and exhibit characteristic expression patterns associated with adaptive (γδTn), IFN-γ-producing (γδT1) and IFN-γ/IL-4-co-producing γδ T cells (γδNKT). Developmental progression towards both IFN-γ-producing subsets can be induced by TCR signalling, and each pathway results in thymic emigration at a different stage. Finally, we show that γδT1 cells are the predominating IFN-γ-producing subset developing in the adult thymus. Thus, this study maps out three distinct development pathways that result in the programming of γδTn, γδT1 and γδNKT cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

