Identification of insulin-sensitizing molecules acting by disrupting the interaction between the Insulin Receptor and Grb14
- PMID: 29203791
- PMCID: PMC5715071
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-17122-6
Identification of insulin-sensitizing molecules acting by disrupting the interaction between the Insulin Receptor and Grb14
Abstract
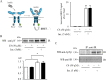
Metabolic diseases are characterized by a decreased action of insulin. During the course of the disease, usual treatments frequently fail and patients are finally submitted to insulinotherapy. There is thus a need for innovative therapeutic strategies to improve insulin action. Growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (Grb14) is a molecular adapter that specifically binds to the activated insulin receptor (IR) and inhibits its tyrosine kinase activity. Molecules disrupting Grb14-IR binding are therefore potential insulin-sensitizing agents. We used Structure-Based Virtual Ligand Screening to generate a list of 1000 molecules predicted to hinder Grb14-IR binding. Using an acellular bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) assay, we identified, out of these 1000 molecules, 3 compounds that inhibited Grb14-IR interaction. Their inhibitory effect on insulin-induced Grb14-IR interaction was confirmed in co-immunoprecipitation experiments. The more efficient molecule (C8) was further characterized. C8 increased downstream Ras-Raf and PI3-kinase insulin signaling, as shown by BRET experiments in living cells. Moreover, C8 regulated the expression of insulin target genes in mouse primary hepatocytes. These results indicate that C8, by reducing Grb14-IR interaction, increases insulin signalling. The use of C8 as a lead compound should allow for the development of new molecules of potential therapeutic interest for the treatment of diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Interaction between the insulin receptor and Grb14: a dynamic study in living cells using BRET.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 30;72(11):1355-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.018. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16934761
-
Molecular determinants of Grb14-mediated inhibition of insulin signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jul;23(7):1043-51. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0360. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19359342 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction with Grb14 results in site-specific regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor.EMBO Rep. 2006 May;7(5):512-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400668. Epub 2006 Mar 31. EMBO Rep. 2006. PMID: 16582879 Free PMC article.
-
[Control of insulin signalisation and action by the Grb14 protein].Biol Aujourdhui. 2014;208(2):119-36. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2014013. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Biol Aujourdhui. 2014. PMID: 25190572 Review. French.
-
Regulation and functional roles of Grb14.Front Biosci. 2004 May 1;9:1626-36. doi: 10.2741/1228. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14977573 Review.
Cited by
-
S-Allylmercaptocysteine improves alcoholic liver disease partly through a direct modulation of insulin receptor signaling.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Mar;11(3):668-679. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.11.006. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33777674 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Grb14, a negative modulator of insulin signaling, improves glucose homeostasis without causing cardiac dysfunction.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 25;10(1):3417. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60290-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32099031 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2025 Jul;21(7):413-426. doi: 10.1038/s41574-025-01114-y. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40247011 Review.
-
Novel Linkage Peaks Discovered for Diabetic Nephropathy in Individuals With Type 1 Diabetes.Diabetes. 2021 Apr;70(4):986-995. doi: 10.2337/db20-0158. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33414249 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Screening and Experimental Validation of Inhibitor Targeting the Complex Formation of Grb14 and Insulin Receptor.Molecules. 2023 Dec 29;29(1):198. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010198. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Combettes-Souverain M, Issad T. Molecular basis of insulin action. Diabetes Metab. 1998;24:477–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

