Interleukin-13 receptor alpha 2 cooperates with EGFRvIII signaling to promote glioblastoma multiforme
- PMID: 29203859
- PMCID: PMC5715073
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01392-9
Interleukin-13 receptor alpha 2 cooperates with EGFRvIII signaling to promote glioblastoma multiforme
Abstract
The interleukin-13 receptor alpha2 (IL-13Rα2) is a cancer-associated receptor overexpressed in human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). This receptor is undetectable in normal brain which makes it a highly suitable target for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. However, the pathological role of this receptor in GBM remains to be established. Here we report that IL-13Rα2 alone induces invasiveness of human GBM cells without affecting their proliferation. In contrast, in the presence of the mutant EGFR (EGFRvIII), IL-13Rα2 promotes GBM cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, the cytoplasmic domain of IL-13Rα2 specifically binds to EGFRvIII, and this binding upregulates the tyrosine kinase activity of EGFRvIII and activates the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and STAT3 pathways. Our findings support the "To Go or To Grow" hypothesis whereby IL-13Rα2 serves as a molecular switch from invasion to proliferation, and suggest that targeting both receptors with STAT3 signaling inhibitor might be a therapeutic approach for the treatment of GBM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
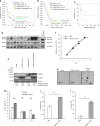


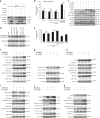

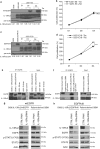

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

