Spontaneous Spinal Discitis and Spondylodiscitis: Clinicotherapeutic Remarks
- PMID: 29204028
- PMCID: PMC5709891
- DOI: 10.4103/jnrp.jnrp_67_17
Spontaneous Spinal Discitis and Spondylodiscitis: Clinicotherapeutic Remarks
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
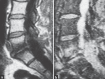
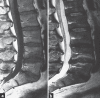
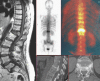
Figures
References
-
- Ledermann HP, Schweitzer ME, Morrison WB, Carrino JA. MR imaging findings in spinal infections: Rules or myths? Radiology. 2003;228:506–14. - PubMed
-
- Modic MT, Feiglin DH, Piraino DW, Boumphrey F, Weinstein MA, Duchesneau PM, et al. Vertebral osteomyelitis: Assessment using MR. Radiology. 1985;157:157–66. - PubMed
-
- Nussbaum ES, Rigamonti D, Standiford H, Numaguchi Y, Wolf AL, Robinson WL. Spinal epidural abscess: A report of 40 cases and review. Surg Neurol. 1992;38:225–31. - PubMed
-
- Pereira CE, Lynch JC. Spinal epidural abscess: An analysis of 24 cases. Surg Neurol. 2005;63(Suppl 1):S26–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
