Pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor modulate differently CYP3A-mediated metabolism in early- and late-stage cholestasis
- PMID: 29204052
- PMCID: PMC5698245
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7519
Pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor modulate differently CYP3A-mediated metabolism in early- and late-stage cholestasis
Abstract
Aim: To ascertain whether cholestasis affects the expression of two CYP3A isoforms (CYP3A1 and CYP3A2) and of pregnane X receptor (PXR) and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR).
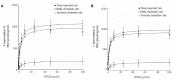
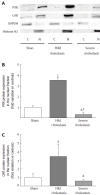
Methods: Cholestasis was induced by bile duct ligation in 16 male Wistar rats; whereas 8 sham-operated rats were used as controls. Severity of cholestasis was assessed on histological examination of liver sections, and serum concentrations of albumin, AST, ALT, GGT, ALPK and bilirubin. Gene and protein expressions of PXR, CAR, CYP3A1 and CYP3A2 were assessed by means of qRT-PCR and Western blot, respectively. Alterations in CYP3A activity were measured by calculating the kinetic parameters of 4-OH and 1'-OH-midazolam hydroxylation, marker reactions for CYP3A enzymes.
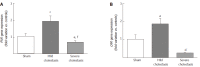
Results: The mRNA and protein expression of CYP3A1 increased significantly in mild cholestasis (P < 0.01). At variance, mRNA and protein expression of CYP3A2 didn't change in mild cholestasis, whereas the expression and activity of both CYP3A1 and CYP3A2 decreased dramatically when cholestasis became severe. Consistently with these observations, the nuclear expression of both PXR and CAR, which was measured because they both translocate into the cell nucleus after their activation, virtually disappeared in the late stage of cholestatic injury, after an initial increase. These results indicate that early- and late-stage cholestasis affects CYP3A-mediated drug metabolism differently, probably as consequence of the different activation of PXR and CAR.
Conclusion: Early- and late-stage cholestasis affects CYP3A-mediated drug metabolism differently. PXR and CAR might be targeted therapeutically to promote CYP3A-mediated liver detoxification.
Keywords: CYP3A; Cholestasis; Constitutive androstane receptor; Drug metabolism; Pregnane X receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures



References
-
- Trauner M, Meier PJ, Boyer JL. Molecular pathogenesis of cholestasis. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1217–1227. - PubMed
-
- Hirschfield GM, Heathcote EJ, Gershwin ME. Pathogenesis of cholestatic liver disease and therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1481–1496. - PubMed
-
- Poupon R. Ursodeoxycholic acid and bile-acid mimetics as therapeutic agents for cholestatic liver diseases: an overview of their mechanisms of action. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2012;36 Suppl 1:S3–S12. - PubMed
-
- Trauner M, Halilbasic E. Nuclear receptors as new perspective for the management of liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1120–1125.e1-12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

