Pallister-Hall Syndrome
- PMID: 29204208
- PMCID: PMC5696670
- DOI: 10.4103/jpn.JPN_101_17
Pallister-Hall Syndrome
Abstract
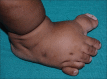
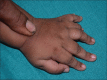
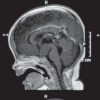
Polydactyly is a relatively common abnormality in infants. However, it can be a marker of a wide variety of neurological and systemic abnormality. Hence, it is important for pediatrician and physician to have insight into the various association of this apparently innocuous anomaly. In this write-up, we report an extremely rare syndrome associated with polydactyly that is Pallister-Hall syndrome. A 10-month-old male child born by lower segment cesarean section presented with global delay associated with microcephaly, frontal bossing, hypertelorism, flat nose, short philtrum, incomplete cleft in the upper lip and hard palate, polydactyly, and syndactyly. The child presented with repeated vomiting and crying episodes. The patient was investigated which revealed a hypothalamic hamartomas. Pallister-Hall syndrome is a very rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder due to mutation in GLI3 gene in the short arm of chromosome 7 with variable penetrance and expressivity.
Keywords: Hypothalamic hamartomas; Laurence–Moon–Biedl syndrome; Pallister–Hall syndrome; polydactyly.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Watson BT, Hennrikus WL. Postaxial type-B polydactyly. Prevalence and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79:65–8. - PubMed
-
- Castilla EE, Lugarinho R, da Graça Dutra M, Salgado LJ. Associated anomalies in individuals with polydactyly. Am J Med Genet. 1998;80:459–65. - PubMed
-
- Itrović B, Rozema LA. On the correct formula for the lifetime broadened superconducting density of states. J Phys Condens Matter. 2007;20:015215.
-
- Kulkarni ML, Rajendran NK, Sangam DK. Inner canthal, outer canthal and inter pupillary distance in newborns. Indian Pediatr. 1992;29:759–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

