Roles and Mechanisms of Herbal Medicine for Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Current Status and Perspective
- PMID: 29204251
- PMCID: PMC5674516
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8214541
Roles and Mechanisms of Herbal Medicine for Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Current Status and Perspective
Abstract
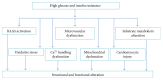
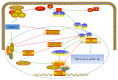
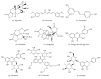
Diabetic cardiomyopathy is one of the major complications among patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is featured by left ventricular hypertrophy, myocardial fibrosis, and damaged left ventricular systolic and diastolic functions. The pathophysiological mechanisms include metabolic-altered substrate metabolism, dysfunction of microvascular, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) activation, oxidative stress, cardiomyocyte apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and impaired Ca2+ handling. An array of molecules and signaling pathways such as p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and extracellular-regulated protein kinases (ERK) take roles in the pathogenesis of DCM. Currently, there was no remarkable effect in the treatment of DCM with application of single Western medicine. The myocardial protection actions of herbs have been gearing much attention. We present a review of the progress research of herbal medicine as a potential therapy for diabetic cardiomyopathy and the underlying mechanisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 8;17(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122001. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27941647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of p38 MAPK in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 30;17(7):1037. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071037. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27376265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Effect of mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy and intervention of traditional Chinese medicine].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Jan;43(1):8-14. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20171027.014. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29552805 Review. Chinese.
-
MicroRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in the pathophysiological processes of diabetic cardiomyopathy: emerging biomarkers and potential therapeutics.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Feb 27;20(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01245-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33639953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early administration of trimetazidine attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats by alleviating fibrosis, reducing apoptosis and enhancing autophagy.J Transl Med. 2016 Apr 27;14(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0849-1. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27121077 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Food-borne Lactiplantibacillus plantarum protect normal intestinal cells against inflammation by modulating reactive oxygen species and IL-23/IL-17 axis.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 1;10(1):16340. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73201-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33004903 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of herbal extracts for TLR2- and TLR4-dependent anti-inflammatory effects.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 11;13(10):e0203907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203907. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30307962 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of hederagenin on diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting NF-κB and Smads signaling pathways in a type-2 diabetic mice model.RSC Adv. 2019 Aug 21;9(45):26238-26247. doi: 10.1039/c9ra02043h. eCollection 2019 Aug 19. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35531007 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclocarya paliurus ethanol leaf extracts protect against diabetic cardiomyopathy in db/db mice via regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling.Food Nutr Res. 2020 Aug 31;64. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v64.4267. eCollection 2020. Food Nutr Res. 2020. PMID: 33061882 Free PMC article.
-
Promising Therapeutic Treatments for Cardiac Fibrosis: Herbal Plants and Their Extracts.Cardiol Ther. 2023 Sep;12(3):415-443. doi: 10.1007/s40119-023-00319-4. Epub 2023 May 29. Cardiol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37247171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

