Acid suppressive therapy improved symptoms due to circumferential cervical inlet patch with proton pumps (H+/K+-ATPase)
- PMID: 29204429
- PMCID: PMC5700390
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v5.i11.403
Acid suppressive therapy improved symptoms due to circumferential cervical inlet patch with proton pumps (H+/K+-ATPase)
Abstract
Cervical inlet patch (CIP), also referred to as esophageal heterotopic gastric mucosa, is regarded as the residue of columnar epithelium of the embryonic esophagus. Narrow band imaging increases the detection rate of CIP. Herein, we present a 55-year-old man with symptomatic circumferential inlet patch. He exhibited globus and dysphagia, and esophagogastroduodenoscopy found cir-cumferential CIP, where im-munohistochemistry revealed the existence of pro-ton pumps (H+, K+-ATPase). His throat symptoms were relieved by acid suppressive therapy with pump inhibitors. This case indicated that CIP should be considered as a differential diagnosis for the cause of globus symptoms in rare cases.
Keywords: Cervical inlet patch; Proton pump inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No conflict interest to declare.
Figures
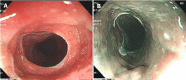
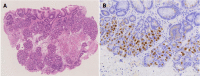
References
-
- von Rahden BH, Stein HJ, Becker K, Liebermann-Meffert D, Siewert JR. Heterotopic gastric mucosa of the esophagus: literature-review and proposal of a clinicopathologic classification. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:543–551. - PubMed
-
- Hori K, Kim Y, Sakurai J, Watari J, Tomita T, Oshima T, Kondo C, Matsumoto T, Miwa H. Non-erosive reflux disease rather than cervical inlet patch involves globus. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:1138–1145. - PubMed
-
- Galan AR, Katzka DA, Castell DO. Acid secretion from an esophageal inlet patch demonstrated by ambulatory pH monitoring. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:1574–1576. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

