Clinicopathological significance of p16, cyclin D1, Rb and MIB-1 levels in skull base chordoma and chondrosarcoma
- PMID: 29204540
- PMCID: PMC5698503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.wjorl.2015.09.005
Clinicopathological significance of p16, cyclin D1, Rb and MIB-1 levels in skull base chordoma and chondrosarcoma
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the expression of p16, cyclin D1, retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (Rb) and MIB-1 in skull base chordoma and chondrosarcoma tissues, and to determine the clinicopathological significance of the above indexes in these diseases.
Methods: A total of 100 skull base chordoma, 30 chondrosarcoma, and 20 normal cartilage tissue samples were analyzed by immunohistochemistry. The expression levels of p16, cyclinD1, Rb and MIB-1 proteins were assessed for potential correlation with the clinicopathological features.
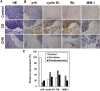
Results: As compared to normal cartilage specimen (control), there was decreased expression of p16, and increased expression of cyclin D1, Rb and MIB-1 proteins, in both skull base chordoma and chondrosarcoma specimens. MIB-1 LI levels were significantly increased in skull base chordoma specimens with negative expression of p16, and positive expression of cyclin D1 and Rb (P < 0.05). Significantly elevated MIB-1 LI was also detected in skull base chondrosarcoma tissues, while there was negative expression of p16, cyclin D1 and Rb (P < 0.05). In skull base chordoma, p16 negatively correlated with cyclin D1 and Rb, while cyclin D1 positively correlated with Rb. Additionally, p16, cyclin D1, Rb, or MIB-1 expression showed no correlation with age, gender, or pathological classification of patients with skull base chordoma (P > 0.05). However, p16 and MIB-1 levels correlated with the intradural invasion, and expression of p16, Rb and MIB-1 correlated with the number of tumor foci (P < 0.05). Further, the expression of p16 and MIB-1 appeared to correlate with the prognosis of patients with skull base chordoma.
Conclusions: The abnormal expression of p16, cyclin D1 and Rb proteins might be associated with the tumorigenesis of skull base chordoma and chondrosarcoma.
Keywords: Cyclin D1; MIB-1; Rb; Skull base chondrosarcoma; Skull base chordoma; p16.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of cyclin D1, p16 and retinoblastoma protein expressions with prognosis and metastasis of gallbladder carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Feb 7;11(5):744-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i5.744. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15655836 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of G1-S checkpoint in chordoma: the prognostic impact of p53 overexpression.Cancer. 2005 Sep 15;104(6):1255-63. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21296. Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16078265
-
[The expression of Rb, p16 and cyclin D1 in 41 esophageal cancers].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 1996 Dec;25(6):336-9. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 1996. PMID: 9388858 Chinese.
-
Alterations of expression of Rb, p16(INK4A) and cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung carcinoma and their clinical significance.J Pathol. 1999 Aug;188(4):351-60. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199908)188:4<351::AID-PATH385>3.0.CO;2-W. J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10440744
-
Chondroid chordoma versus low-grade chondrosarcoma of the base of the skull: can immunohistochemistry resolve the controversy?J Neurooncol. 1994;18(3):199-206. doi: 10.1007/BF01328954. J Neurooncol. 1994. PMID: 7525890 Review.
Cited by
-
A correlation analysis of sacrococcygeal chordoma imaging and clinical characteristics with the prognostic factors.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 26;12:1012918. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1012918. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36226065 Free PMC article.
-
Low expression of H3K27me3 is associated with poor prognosis in conventional chordoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 19;12:1048482. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1048482. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36601478 Free PMC article.
-
Y-box binding protein-1 promotes tumorigenesis and progression via the epidermal growth factor receptor/AKT pathway in spinal chordoma.Cancer Sci. 2019 Jan;110(1):166-179. doi: 10.1111/cas.13875. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30426615 Free PMC article.
-
Latest Developments in Targeted Biological Therapies in the Management of Chordoma and Chondrosarcoma.Global Spine J. 2025 Jan;15(1_suppl):120S-131S. doi: 10.1177/21925682241227917. Global Spine J. 2025. PMID: 39801117 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of p16 and cyclin D1 expression with the incidence and prognosis of cardiac carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jun;17(6):4859-4864. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10189. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31186693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almefty K., Pravdenkova S., Colli B.O. Chordoma and chondrosarcoma: similar, but quite different, skull base tumors. Cancer. 2007;110:2457–2467. - PubMed
-
- Van Gompel J.J., Janus J.R. Chordoma and chondrosarcoma. Otolaryngol Clin N Am. 2015;48:501–514. - PubMed
-
- Gagliardi F., Boari N., Riva P. Current therapeutic options and novel molecular markers in skull base chordomas. Neurosurg Rev. 2012;35:1–13. discussion 13–14. - PubMed
-
- Jahangiri A., Jian B., Miller L. Skull base chordomas: clinical features, prognostic factors, and therapeutics. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2013;24:79–88. - PubMed
-
- Lanzino G., Dumont A.S., Lopes M.B. Skull base chordomas: overview of disease, management options, and outcome. Neurosurg Focus. 2001;10:E12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

