Repeated shock stress facilitates basolateral amygdala synaptic plasticity through decreased cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase type IV (PDE4) expression
- PMID: 29204911
- PMCID: PMC5886824
- DOI: 10.1007/s00429-017-1575-z
Repeated shock stress facilitates basolateral amygdala synaptic plasticity through decreased cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase type IV (PDE4) expression
Abstract
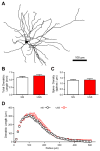
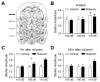
Previous studies have shown that exposure to stressful events can enhance fear memory and anxiety-like behavior as well as increase synaptic plasticity in the rat basolateral amygdala (BLA). We have evidence that repeated unpredictable shock stress (USS) elicits a long-lasting increase in anxiety-like behavior in rats, but the cellular mechanisms mediating this response remain unclear. Evidence from recent morphological studies suggests that alterations in the dendritic arbor or spine density of BLA principal neurons may underlie stress-induced anxiety behavior. Recently, we have shown that the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in BLA principal neurons is dependent on activation of postsynaptic D1 dopamine receptors and the subsequent activation of the cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate (cAMP)-protein kinase A (PKA) signaling cascade. Here, we have used in vitro whole-cell patch-clamp recording from BLA principal neurons to investigate the long-term consequences of USS on their morphological properties and synaptic plasticity. We provided evidence that the enhanced anxiety-like behavior in response to USS was not associated with any significant change in the morphological properties of BLA principal neurons, but was associated with a changed frequency dependence of synaptic plasticity, lowered LTP induction threshold, and reduced expression of phosphodiesterase type 4 enzymes (PDE4s). Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition of PDE4 activity with rolipram mimics the effects of chronic stress on LTP induction threshold and baseline startle. Our results provide the first evidence that stress both enhances anxiety-like behavior and facilitates synaptic plasticity in the amygdala through a common mechanism of PDE4-mediated disinhibition of cAMP-PKA signaling.
Keywords: Basolateral amygdala; Chronic stress; Compartmentalization; Macromolecular complexes; Morphology; a-Kinase anchoring protein.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Synergistic activation of dopamine D1 and TrkB receptors mediate gain control of synaptic plasticity in the basolateral amygdala.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026065. Epub 2011 Oct 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22022509 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and functional changes in the preweaning basolateral amygdala induced by early chronic stress associate with anxiety and fear behavior in adult male, but not female rats.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 2;81:25-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.09.025. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 28963066
-
Compartmentalized PDE4A5 Signaling Impairs Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Long-Term Memory.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 24;36(34):8936-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0248-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27559174 Free PMC article.
-
Role of stress, corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) and amygdala plasticity in chronic anxiety.Stress. 2005 Dec;8(4):209-19. doi: 10.1080/10253890500504557. Stress. 2005. PMID: 16423710 Review.
-
Regulation of conditioned responses of basolateral amygdala neurons.Physiol Behav. 2002 Dec;77(4-5):489-93. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(02)00909-5. Physiol Behav. 2002. PMID: 12526988 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of stress on AMPA receptor distribution and function in the basolateral amygdala.Brain Struct Funct. 2014 Jul;219(4):1169-79. doi: 10.1007/s00429-013-0557-z. Epub 2013 May 5. Brain Struct Funct. 2014. PMID: 23644586 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid actions on synapses, circuits, and behavior: implications for the energetics of stress.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014 Apr;35(2):180-196. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24361584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAN-selective inhibition of cAMP-phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) induces gastroparesis in mice.FASEB J. 2020 Sep;34(9):12533-12548. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001016RR. Epub 2020 Aug 1. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32738081 Free PMC article.
-
Late-Onset Behavioral and Synaptic Consequences of L-Type Ca2+ Channel Activation in the Basolateral Amygdala of Developing Rats.eNeuro. 2022 Feb 22;9(1):ENEURO.0282-21.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0282-21.2022. Print 2022 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35064022 Free PMC article.
-
PDE4B Missense Variant Increases Susceptibility to Post-traumatic Stress Disorder-Relevant Phenotypes in Mice.J Neurosci. 2024 Oct 23;44(43):e0137242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0137-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39256048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abercrombie HC, Schaefer SM, Larson CL, Oakes TR, Lindgren KA, et al. Metabolic rate in the right amygdala predicts negative affect in depressed patients. Neuroreport. 1998;9:3301–3307. - PubMed
-
- Baillie GS, Houslay MD. Arrestin times for compartmentalised cAMP signalling and phosphodiesterase-4 enzymes. Curr Opin Cel Biol. 2005;17(2):129–134. - PubMed
-
- Beylin AV, Shors TJ. Stress enhances excitatory trace eyeblink conditioning and opposes acquisition of inhibitory conditioning. Behav Neurosci. 1998;112:1327–1338. - PubMed
-
- Blair HT, Schafe GE, Bauer EP, Rodrigues SM, LeDoux JE. Synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala: a cellular hypothesis of fear conditioning. Learn Mem. 2001;8:229–242. - PubMed
-
- Blitzer RD, Wong T, Nouranifar R, Iyengar R, Landau EM. Postsynaptic cAMP pathway gates early LTP in hippocampal CA1 region. Neuron. 1995;15:1403–1414. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

