Circulating microRNA signature of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- PMID: 29205600
- PMCID: PMC6528947
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12418
Circulating microRNA signature of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Abstract
Objectives: Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) is a common orthopaedic disease of which early detection remains clinically challenging. Accumulating evidences indicated that circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) plays vital roles in the development of several bone diseases. However, the association between circulating miRNAs and steroid-induced ONFH remains elusive.
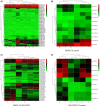
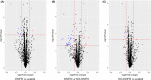
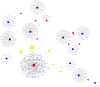
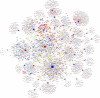
Materials and methods: miRNA microarray was performed to identify the differentially abundant miRNAs in the serums of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients with steroid-induced ONFH as compared with SLE control and healthy control group. We predicted the potential functions of these differentially abundant miRNAs using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses and reconstructed the regulatory networks of miRNA-mRNA interactions.
Results: Our data indicated that there were 11 differentially abundant miRNAs (2 upregulated and 9 downregulated) between SLE-ONFH group and healthy control group and 42 differentially abundant miRNAs (14 upregulated and 28 downregulated) between SLE-ONFH group and SLE control group. We also predicted the potential functions of these differentially abundant miRNAs using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses and reconstructed the regulatory networks of miRNA-mRNA interactions.
Conclusions: These findings corroborated the idea that circulating miRNAs play significant roles in the development of ONFH and may serve as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: GO; KEGG; ONFH; circulating microRNAs; osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Liu XL, Li Q, Sheng JG, et al. Unique plasma metabolomic signature of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res. 2016;34:1158‐1167. - PubMed
-
- Kuroda Y, Asada R, So K, et al. A pilot study of regenerative therapy using controlled release of recombinant human fibroblast growth factor for patients with pre‐collapse osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int Orthop. 2016;40:1747‐1754. - PubMed
-
- Okura T, Hasegawa Y, Morita D, Osawa Y, Ishiguro N. What factors predict the failure of curved intertrochanteric varus osteotomy for the osteonecrosis of the femoral head? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136:1647‐1655. - PubMed
-
- Kubo T, Ueshima K, Saito M, Ishida M, Arai Y, Fujiwara H. Clinical and basic research on steroid‐induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21:407‐413. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

