Effects of kartogenin on the attenuated nucleus pulposus cell degeneration of intervertebral discs induced by interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α
- PMID: 29207013
- PMCID: PMC5752177
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3283
Effects of kartogenin on the attenuated nucleus pulposus cell degeneration of intervertebral discs induced by interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α
Abstract
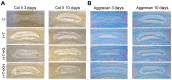
Cytokines are the main cause of intervertebral disc degeneration. Kartogenin (KGN) is found to protect chondrocytes from cytokines. To explore whether KGN can slow down the degeneration on intervertebral discs following exposure to interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF‑α), the expression of type II collagen (Col II) and aggrecan were detected by immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry and tissue staining. An in vitro model of disc degeneration using human nucleus pulposus cells (hNPCs) and ex vivo culture of mouse intervertebral discs organs under the actions of inflammatory cytokines were used, and the expression of Col II and aggrecan in hNPCs were detected by semi-quantitative western blot analysis, and the mRNA expression of the genes than encode Col II and aggrecan were detected by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The results indicated that the expression of Col II and aggrecan was reduced in the degeneration models. However, the protein expressions of Col II and aggrecan were significantly elevated in hNPCs and the mouse intervertebral discs following addition of KGN. RT-qPCR results revealed that the mRNA expression of Col II and aggrecan was increased in hNPCs and mouse intervertebral discs following treatment with KGN. Thus, KGN effectively increased the expression of Col II and aggrecan in hNPCs and slowed the degeneration of intervertebral discs stimulated by IL-1β and TNF-α.
Figures





References
-
- Katz JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg A. 2006;88(Suppl 2):21–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

