Steppogenin Isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata Shows Antineuroinflammatory Effects via NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV2 and Primary Rat Microglial Cells
- PMID: 29207498
- PMCID: PMC6149939
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22122130
Steppogenin Isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata Shows Antineuroinflammatory Effects via NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV2 and Primary Rat Microglial Cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: Kim, D.-C.; et al. Steppogenin Isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata Shows Antineuroinflammatory Effects via NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV2 and Primary Rat Microglial Cells. Molecules 2017, 22, 2130.Molecules. 2018 May 23;23(6):1244. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061244. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29882855 Free PMC article.
Abstract
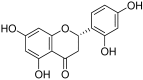
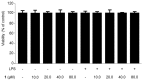
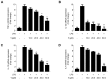
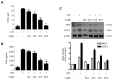
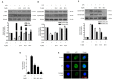
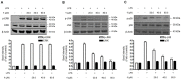
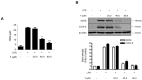
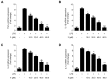
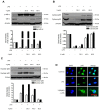
Excessive microglial stimulation has been recognized in several neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson's disease (PD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), amyotropic lateral sclerosis (ALS), HIV-associated dementia (HAD), multiple sclerosis (MS), and stroke. When microglia are stimulated, they produce proinflammatory mediators and cytokines, including nitric oxide (NO) derived from inducible NO synthase (iNOS), prostaglandin E2 (PGE₂) derived from cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-12 (IL-12), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These inflammatory reactions are related to the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. Therefore, the modulation of NF-κB and MAPK is vital to prevent microglial activation and confer resistance against neuronal injury. In this study, steppogenin (1) isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata suppressed the neuroinflammatory responses to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Steppogenin (1) inhibited the production of proinflammatory mediators and cytokines in LPS-challenged BV2 and rat primary microglial cells. Moreover, western blot analysis and immunofluorescence revealed that the nuclear translocation of NF-κB was inhibited in LPS-induced BV2 and rat primary microglial cells. The LPS-stimulated activation of BV2 and rat primary microglial cells was inhibited by steppogenin (1) through the suppression of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAPK signaling. These results suggested that steppogenin (1) exerted antineuroinflammatory effects against acute neuroinflammation in BV2 and rat primary microglial cells by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling and the production of proinflammatory mediators and cytokines.
Keywords: Cudrania tricuspidata; mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); neuroinflammation; nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB); steppogenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LXW7 attenuates inflammation via suppressing Akt/nuclear factor kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Dec;77:105963. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105963. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31732449
-
Prenylated Flavonoids from Cudrania tricuspidata Suppress Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammatory Activities in BV2 Microglial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 19;17(2):255. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020255. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26907256 Free PMC article.
-
Nardosinone-Type Sesquiterpenes from the Hexane Fraction of Nardostachys jatamansi Attenuate NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells.Inflammation. 2018 Aug;41(4):1215-1228. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0768-9. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29616391
-
Nuclear Factor Kappa B: A Nobel Therapeutic Target of FlavonoidsAgainst Parkinson's Disease.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(14):2062-2077. doi: 10.2174/0113862073295568240105025006. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 38243959 Review.
-
Pharmacological modulation of cytokines correlating neuroinflammatory cascades in epileptogenesis.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1437-1452. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06896-8. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34751915 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Uremic Clearance Granules on p38 MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway, Microbial and Metabolic Profiles in End-Stage Renal Disease Rats Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Aug 3;16:2529-2544. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S364069. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35946040 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the brain‑gut axis on neuroinflammation in cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion injury (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Mar;53(3):30. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5354. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38299236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia in motor neuron disease: Signaling evidence from last 10 years.Dev Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;82(7-8):625-638. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22905. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Dev Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36309345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Model yeast as a versatile tool to examine the antioxidant and anti-ageing potential of flavonoids, extracted from medicinal plants.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 2;13:980066. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.980066. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120300 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy and apoptosis cascade: which is more prominent in neuronal death?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):8001-8047. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04004-4. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34741624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi S.R., You D.H., Kim J.Y., Park C.B., Kim D.H., Ryu J. Antioxidant activity of methanol extracts from Cudrania tricuspidata Bureau according to harvesting parts and time. Korean J. Med. Crop. Sci. 2009;17:115–120.
-
- Shougakukan . The Dictionary of Chinese Drugs. Shanghai Science and Technological Publisher; Shanghai, China: 1985.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

