TXNDC5 is a cervical tumor susceptibility gene that stimulates cell migration, vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis by down-regulating SERPINF1 and TRAF1 expression
- PMID: 29207620
- PMCID: PMC5710901
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18857
TXNDC5 is a cervical tumor susceptibility gene that stimulates cell migration, vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis by down-regulating SERPINF1 and TRAF1 expression
Abstract
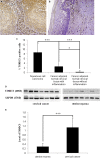
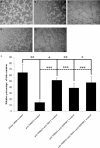
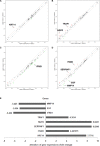
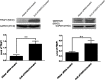
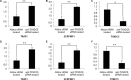
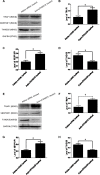
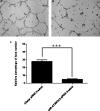
TXNDC5 (thioredoxin domain-containing protein 5) catalyzes disulfide bond formation, isomerization and reduction. Studies have reported that TXNDC5 expression is increased in some tumor tissues and that its increased expression can predict a poor prognosis. However, the tumorigenic mechanism has not been well characterized. In this study, we detected a significant association between the rs408014 and rs7771314 SNPs at the TXNDC5 locus and cervical carcinoma using the Taqman genotyping method. We also detected a significantly increased expression of TXNDC5 in cervical tumor tissues using immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. Additionally, inhibition of TXNDC5 expression using siRNA prevented tube-like structure formation, an experimental indicator of vasculogenic mimicry and metastasis, in HeLa cervical tumor cells. Inhibiting TXNDC5 expression simultaneously led to the increased expression of SERPINF1 (serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F) and TRAF1 (TNF receptor-associated factor 1), which have been reported to inhibit angiogenesis and metastasis as well as induce apoptosis. This finding was confirmed in Caski and C-33A cervical tumor cell lines. The ability to form tube-like structures was rescued in HeLa cells simultaneously treated with anti-TXNDC5, SERPINF1 and TRAF1 siRNAs. Furthermore, the inhibition of TXNDC5 expression significantly attenuated endothelial tube formation, a marker of angiogenesis, in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The present study suggests that TXNDC5 is a susceptibility gene in cervical cancer, and high expression of this gene contributes to abnormal angiogenesis, vasculogenic mimicry and metastasis by down-regulating SERPINF1 and TRAF1 expression.
Keywords: SERPINF1; TRAF1; TXNDC5; cervical tumor; pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None of the authors have a financial interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in tumors.Int J Oncol. 2013 Dec;43(6):1871-84. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2123. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24100949
-
High TXNDC5 expression predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jul;37(7):9797-806. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-4891-7. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26810069
-
[TXNDC5 mediates serum starvation-induced proliferation inhibition of HeLa cell].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2014 Oct;36(5):470-6. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2014.05.003. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25360642 Chinese.
-
Thioredoxin Domain Containing 5 (TXNDC5): Friend or Foe?Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 4;46(4):3134-3163. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040197. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in disease progression.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1354952. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354952. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38629066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of four hub genes as promising biomarkers to evaluate the prognosis of ovarian cancer in silico.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jun 24;20:270. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01361-1. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32595417 Free PMC article.
-
TXNDC5 protects synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis from the detrimental effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2020 Feb;9(1):23-29. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2019.01139. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2020. PMID: 32201671 Free PMC article.
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Aug 8;27(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00770-4. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35934705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3 potentiates progression of cervical cancer by suppressing ER stress via regulating m6A modification of TXNDC5 mRNA.Oncogene. 2022 Sep;41(39):4420-4432. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02435-2. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35987795
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Angiogenesis in Development and Tumors Progression: Potential Implications for Cancer Treatment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 6;9:689962. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.689962. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34552922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Powis G, Kirkpatrick DL. Thioredoxin signaling as a targetfor cancer therapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007;7:392–397. - PubMed
-
- Affer M, Chesi M, Chen WD, Keats JJ, Demchenko YN, Tamizhmani K, Garbitt VM, Riggs DL, Brents LA, Roschke AV, Van Wier S, Fonseca R, Bergsagel PL, et al. Promiscuous MYC locus rearrangements hijack enhancers but mostly super-enhancers to dysregulate MYC expression in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2014;28:1725–1735. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang X, Cui Y, Zong M, Zhao Y, Yan X, Chen Y, Han J. Identification of proteins with increased expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:872–880. - PubMed
-
- Noh JY, Oh SH, Lee JH, Kwon YS, Ryu DJ, Lee KH. Can blood components with age-related changes influence the ageing of endothelial cells? Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:339–346. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

