Shp2 regulates migratory behavior and response to EGFR-TKIs through ERK1/2 pathway activation in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 29207630
- PMCID: PMC5710910
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20249
Shp2 regulates migratory behavior and response to EGFR-TKIs through ERK1/2 pathway activation in non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
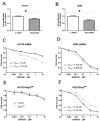
In the clinical treatment of lung cancer, therapy failure is mainly caused by cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Here, we investigated whether the tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 is involved in the development of metastasis and drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Shp2 was overexpressed in a subset of lung cancer tissues, and Shp2 knockdown in lung cancer cells inhibited cell proliferation and migration, downregulated c-Myc and fibronectin expression, and upregulated E-cadherin expression. In H1975 cells, which carry double mutations (L858R + T790M) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) that confers resistance toward the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib, Shp2 knockdown increased cellular sensitivity to gefitinib; conversely, in H292 cells, which express wild-type EGFR and are sensitive to gefitinib, Shp2 overexpression increased cellular resistance to gefitinib. Moreover, by overexpressing Shp2 or using U0126, a small-molecule inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), we demonstrated that Shp2 inhibited E-cadherin expression and enhanced the expression of fibronectin and c-Myc through activation of the ERK1/2 pathway. Our findings reveal that Shp2 is overexpressed in clinical samples of NSCLC and that Shp2 knockdown reduces the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells, and further suggest that co-inhibition of EGFR and Shp2 is an effective approach for overcoming EGFR T790M mutation acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Thus, we propose that Shp2 could serve as a new biomarker in the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: ERK1/2; Shp2; epidermal growth factor receptor; non-small cell lung cancer; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST There are no conflicts interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effect of simvastatin on the resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a non-small cell lung cancer with the T790M mutation of EGFR.Exp Cell Res. 2014 May 1;323(2):288-96. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.02.026. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24631288
-
Effect of siRNAs targeting the EGFR T790M mutation in a non-small cell lung cancer cell line resistant to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors and combination with various agents.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Feb 15;431(3):623-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.070. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23266614
-
Knockdown of the Bcl-2 gene increases sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the H1975 lung cancer cell line harboring T790M mutation.Int J Oncol. 2013 Jun;42(6):2094-102. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1895. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23588221
-
Dacomitinib in lung cancer: a "lost generation" EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitor from a bygone era?Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Oct 15;9:5641-53. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S52787. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26508839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update of the mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer: Gefitinib (Iressa) -induced changes in the expression and nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of HER-ligands (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2007 Jul;20(1):3-10. Int J Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17549382 Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant Expression of miR-362 Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis through Downregulation of Sema3A.J Immunol Res. 2018 Aug 1;2018:1687097. doi: 10.1155/2018/1687097. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30155491 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SHP2/PTPN11 in the occurrence and prognosis of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Oncol Lett. 2022 Nov 22;25(1):19. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13605. eCollection 2023 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36478896 Free PMC article.
-
From Stem to Sternum: The Role of Shp2 in the Skeleton.Calcif Tissue Int. 2023 Apr;112(4):403-421. doi: 10.1007/s00223-022-01042-3. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023. PMID: 36422682 Review.
-
Small molecule inhibitors for cancer immunotherapy and associated biomarkers - the current status.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1297175. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1297175. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical roles of PTPN family members regulated by non-coding RNAs in tumorigenesis and immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 26;12:972906. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.972906. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35957898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262. - DOI - PubMed
-
- D'Amico TA. Angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;16:13–8. - PubMed
-
- Green MR. Targeting targeted therapy. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2191–3. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMe048101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jiang H. Overview of gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer: an Asian perspective. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2009;39:137–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyn139. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buonato JM, Lazzara MJ. ERK1/2 blockade prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells and promotes their sensitivity to EGFR inhibition. Cancer Res. 2014;74:309–19. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-12-4721. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

