Updated treatment strategies for intestinal Behçet's disease
- PMID: 29207867
- PMCID: PMC5768550
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2017.377
Updated treatment strategies for intestinal Behçet's disease
Abstract
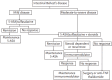
Behçet's disease (BD) is a chronic, idiopathic, relapsing immune-mediated disease involving multiple organs, and is characterized by recurrent oral and genital ulcers, ocular disease, gastrointestinal ulcers, vascular diseases, and skin lesions. In particular, gastrointestinal involvement in BD is followed by severe complications, including massive bleeding, bowel perforation, and fistula, which can lead to significant morbidity and mortality. However, the management of intestinal BD has not yet been properly established. Intestinal BD patients with a severe clinical course experience frequent disease aggravations and often require recurrent corticosteroid and/or immunomodulatory therapies, or even surgery. However, a considerable number of patients with intestinal BD are often refractory to conventional therapies such as corticosteroids and immunomodulators. Recently, there has been a line of evidence suggesting that biologics such as infliximab and adalimumab are effective in treating intestinal BD. Moreover, new biologics targeting proteins other than tumor necrosis factor α are emerging and are under active investigation. Therefore, in this paper, we review the current therapeutic strategies and new clinical data for the treatment of intestinal BD.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Biological products; Infliximab; Intestinal Behcet disease; Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy in Intestinal Behçet's Disease.Gut Liver. 2018 Nov 15;12(6):623-632. doi: 10.5009/gnl17462. Gut Liver. 2018. PMID: 29788675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world efficacy of adalimumab and infliximab for refractory intestinal Behçet's disease.Dig Liver Dis. 2019 Jul;51(7):967-971. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.10.024. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Dig Liver Dis. 2019. PMID: 30872086
-
Diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun;7(3):205-12. doi: 10.1007/s12328-014-0488-0. Epub 2014 Apr 20. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24883128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful combination therapy using adalimumab and 5-aminosalicylic acid for a resistant case of intestinal Behçet's disease.Z Rheumatol. 2020 Sep;79(7):702-706. doi: 10.1007/s00393-020-00816-0. Z Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32494950 English.
-
Update on the Treatment of Behcet's Disease of the Small Bowel with Biologic Agents.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2020 Mar 19;22(5):24. doi: 10.1007/s11894-020-00759-1. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32193746 Review.
Cited by
-
Update on the treatment of Behçet's syndrome.Intern Emerg Med. 2019 Aug;14(5):661-675. doi: 10.1007/s11739-019-02035-1. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Intern Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 30684097 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Infliximab in Intestinal Behçet's Disease: A Multicenter, Phase 3 Study (BEGIN).Gut Liver. 2023 Sep 15;17(5):777-785. doi: 10.5009/gnl220278. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Gut Liver. 2023. PMID: 36578194 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Successful closure of ileostomy in a patient with intestinal Behçet's disease after therapy with adalimumab: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Mar;98(9):e14624. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014624. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30817580 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world effectiveness and safety of adalimumab in Korean patients with intestinal Behcet's disease: a Korean Association for the Study of Intestinal Diseases (KASID) multicenter study.Korean J Intern Med. 2023 Sep;38(5):661-671. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2022.394. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Korean J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37491721 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of corticosteroid monotherapy, and TNF inhibitors with or without corticosteroid in patients with refractory entero-Behcet's disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jun 22;21(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1933-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31228955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheon JH, Kim WH. An update on the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of intestinal Behcet’s disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:24–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical