Meningococcal arthritis and myopericarditis: a case report
- PMID: 29207945
- PMCID: PMC5718011
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2845-3
Meningococcal arthritis and myopericarditis: a case report
Abstract
Background: We report the first adult case of Neisseria meningitidis W-135 presenting with meningococcal arthritis and myopericarditis concomitantly, without other classical features of meningococcal disease.
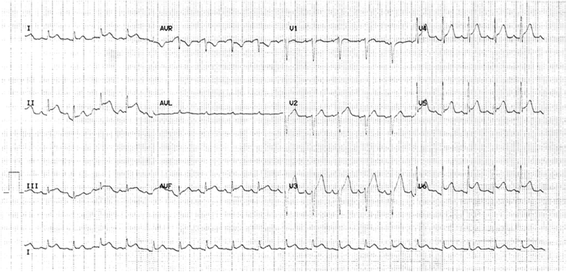
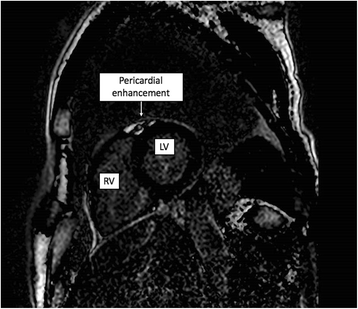
Case presentation: A 67-year-old Caucasian man presented with acute-onset polyarthralgia, myalgia, and fever. On examination he had polyarticular synovitis. An electrocardiogram (ECG) demonstrated ST-elevation in leads I, II, III, aVF, and V2-V6 without reciprocal depression, and a high-sensitivity troponin level was significantly elevated. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging on day five of admission demonstrated patchy pericardial enhancement. Neisseria meningitidis W-135 was isolated from both synovial fluid and blood cultures. The clinical outcome was favourable with intravenous ceftriaxone and myopericarditis treatment (colchicine and ibuprofen).
Conclusions: We conclude that this is a rare case of disseminated Neisseria meningitidis W-135 presenting with acute polyarticular septic arthritis and myopericarditis, without other classical features of systemic meningococcal disease. The earlier described entity of primary meningococcal arthritis (PMA) can present in patients with meningococcal bacteraemia, and may not be distinct from disseminated meningococcal disease, but rather an atypical presentation of this.
Keywords: Arthritis; Infectious; Meningococcal infections; Neisseria meningitidis; Pericarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Patient consent for case report publication in journal and has signed consent form.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Public Health England . Meningococcal reference unit user manual. Manchester: Public Health England; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical