Overexpression of Cullin7 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma progression and pathogenesis
- PMID: 29207970
- PMCID: PMC5718086
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3839-7
Overexpression of Cullin7 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma progression and pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: Overexpression of Cullin7 is associated with some types of malignancies. However, the part of Cullin7 in hepatocellular carcinoma remains unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of Cullin7 in pathogenesis and the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
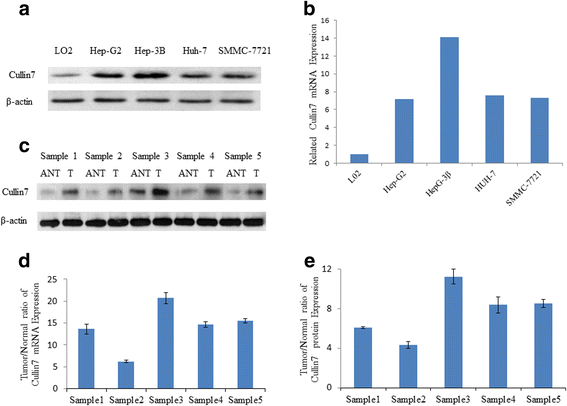
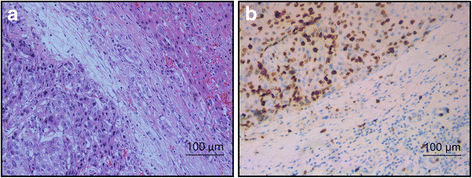
Methods: In the present study, the expression of Cullin7 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and five surgical hepatocellular carcinoma specimens was detected with quantitative reverse transcription PCR and western blotting. In addition, the protein expression of Cullin7 was examined in 162 cases of archived hepatocellular carcinoma using immunohistochemistry.
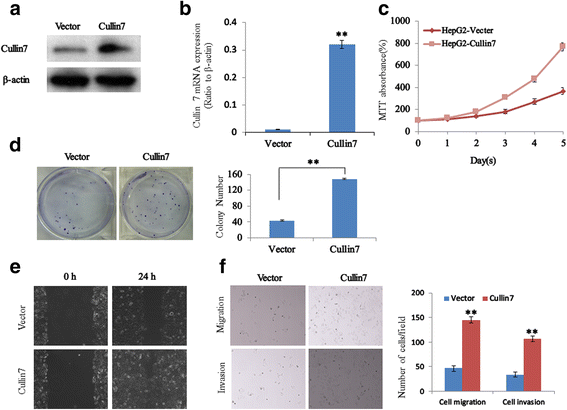
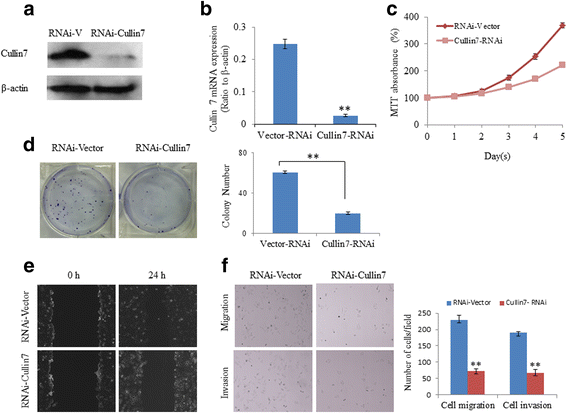
Results: We found elevated expression of both mRNA and protein levels of Cullin7 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, and Cullin7 protein was significantly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma compared with paired normal hepatic tissues. The immunohistochemistry analysis revealed that overexpression of Cullin7 occurred in 69.1% of hepatocellular carcinoma samples, which was a significantly higher rate than that in adjacent normal hepatic tissue (P < 0.01). Statistical analysis found that overexpression of Cullin7 was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, tumor thrombus of the portal vein and advanced clinical stage (P < 0.05). Furthermore, by overexpressing Cullin7 in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells, we revealed that Cullin7 could significantly enhance cell proliferation, growth, migration and invasion. Conversely, knocking down Cullin7 expression with short hairpin RNAi in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells inhibited cell proliferation, growth, migration and invasion.
Conclusion: Our studies provide evidence that overexpression of Cullin7 plays an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and may be a valuable marker for hepatocellular carcinoma management.
Keywords: Cullin7; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Invasion; Proliferation; Western blot.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University. Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of Rabl3 and Cullin7 is associated with pathogenesis and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hum Pathol. 2017 Sep;67:146-151. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28739496
-
The overexpression of Rabl3 is associated with pathogenesis and clinicopathologic variables in hepatocellular carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2017 Apr;39(4):1010428317696230. doi: 10.1177/1010428317696230. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28443498
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor-1α 2 knockdown inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis by suppressing PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 28;22(16):4226-37. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i16.4226. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27122673 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpressed ubiquitin ligase Cullin7 in breast cancer promotes cell proliferation and invasion via down-regulating p53.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Aug 8;450(4):1370-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.06.134. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25003318
-
Inhibition of Liver Carcinoma Cell Invasion and Metastasis by Knockdown of Cullin7 In Vitro and In Vivo.Oncol Res. 2016;23(4):171-81. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14519995067562. Oncol Res. 2016. Retraction in: Oncol Res. 2025 Jul 18;33(8):2179. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.070134. PMID: 27053346 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
Do Salivary Cullin7 Gene Expression and Protein Levels Provide Advantages over Plasma Levels in Diagnosing Breast Cancer?Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Dec 31;47(1):19. doi: 10.3390/cimb47010019. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39852134 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miR-664 is associated with poor overall survival and accelerates cell proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Mar 28;12:2373-2381. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S188658. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30992673 Free PMC article.
-
The functional analysis of Cullin 7 E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer.Oncogenesis. 2020 Oct 31;9(10):98. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00276-w. Oncogenesis. 2020. PMID: 33130829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the roles of neddylation modification in hepatocellular carcinoma: Molecular mechanisms and targeted therapeutics.Genes Dis. 2024 Dec 6;12(4):101483. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101483. eCollection 2025 Jul. Genes Dis. 2024. PMID: 40290125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of HOXA1 in cancer and targeted therapy.Med Oncol. 2025 Aug 4;42(9):405. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02980-2. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40760270 Review.
References
-
- Finkelmeier F, Canli O, Tal A, Pleli T, Trojan J, Schmidt M, Kronenberger B, Zeuzem S, Piiper A, Greten FR, et al. High levels of the soluble programmed death-ligand (sPD-L1) identify hepatocellular carcinoma patients with a poor prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 2016;59:152–159. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.03.002. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

