Protocol for project IMPACT (improving millions hearts for provider and community transformation): a quasi-experimental evaluation of an integrated electronic health record and community health worker intervention study to improve hypertension management among South Asian patients
- PMID: 29207983
- PMCID: PMC5717844
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-017-2767-1
Protocol for project IMPACT (improving millions hearts for provider and community transformation): a quasi-experimental evaluation of an integrated electronic health record and community health worker intervention study to improve hypertension management among South Asian patients
Abstract
Background: The Million Hearts® initiative aims to prevent heart disease and stroke in the United States by mobilizing public and private sectors around a core set of objectives, with particular attention on improving blood pressure control. South Asians in particular have disproportionately high rates of hypertension and face numerous cultural, linguistic, and social barriers to accessing healthcare. Interventions utilizing Health information technology (HIT) and community health worker (CHW)-led patient coaching have each been demonstrated to be effective at advancing Million Hearts® goals, yet few studies have investigated the potential impact of integrating these strategies into a clinical-community linkage initiative. Building upon this initiative, we present the protocol and preliminary results of a research study, Project IMPACT, designed to fill this gap in knowledge.
Methods: Project IMPACT is a stepped wedge quasi-experimental study designed to test the feasibility, adoption, and impact of integrating CHW-led health coaching with electronic health record (EHR)-based interventions to improve hypertension control among South Asian patients in New York City primary care practices. EHR intervention components include the training and implementation of hypertension-specific registry reports, alerts, and order sets. Fidelity to the EHR intervention is assessed by collecting the type, frequency, and utilization of intervention components for each practice. CHW intervention components consist of health coaching sessions on hypertension and related risk factors for uncontrolled hypertensive patients. The outcome, hypertension control (<140 mmHg systolic blood pressure (BP) and <90 mmHg diastolic BP), is collected at the aggregate- and individual-level for all 16 clinical practices enrolled.
Discussion: Project IMPACT builds upon the evidence base of the effectiveness of CHW and Million Hearts® initiatives and proposes a unique integration of provider-based EHR and community-based CHW interventions. The project informs the effectiveness of these interventions in team-based care approaches, thereby, helping to develop relevant sustainability strategies for improving hypertension control among targeted racial/ethnic minority populations at small primary care practices.
Trial registration: This study protocol has been approved and is made available on Clinicaltrials.gov by NCT03159533 as of May 17, 2017.
Keywords: Community health workers (CHWs); Community-clinical linkages; Electronic health record (EHR); Health information technology (HIT); Hypertension; Immigrant health; Million hearts® initiative; South Asians.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Both the EHR and CHW components of this project were submitted to the Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) of the NYU School of Medicine and CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy. NYU’s IRB deemed both components of the project as non-human subjects research, and waived the need for IRB approval. CUNY’s IRB approved both components of the project.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- About Million Hearts ®. Million Hearts Campaign. Health and Human Services. https://millionhearts.hhs.gov/about-million-hearts/index.html. Accessed 29 March 2017.
-
- Valderrama AL, Gillespie C, King SC, George MG, Hong Y, Gregg E. Vital signs: awareness and treatment of uncontrolled hypertension among adults-United States, 2003–2010. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (MMWR) 2012;61(35):703–9. - PubMed
-
- Sokol MC, McGuigan KA, Verbrugge RR, Epstein RS. Impact of medication adherence on hospitalization risk and healthcare cost. Med Care. 2005;43:521–530. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000163641.86870.af. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

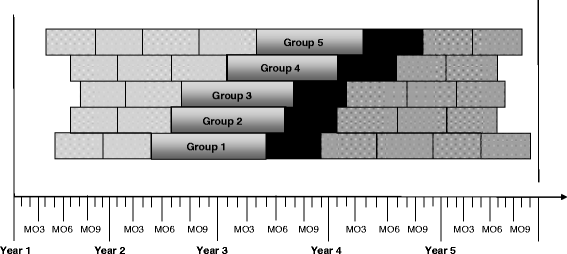
 = Baseline Period (6-month intervals),
= Baseline Period (6-month intervals),  …
…  = Adoption of CHW Intervention,
= Adoption of CHW Intervention,  = Follow-up Data (6-month intervals)
= Follow-up Data (6-month intervals)